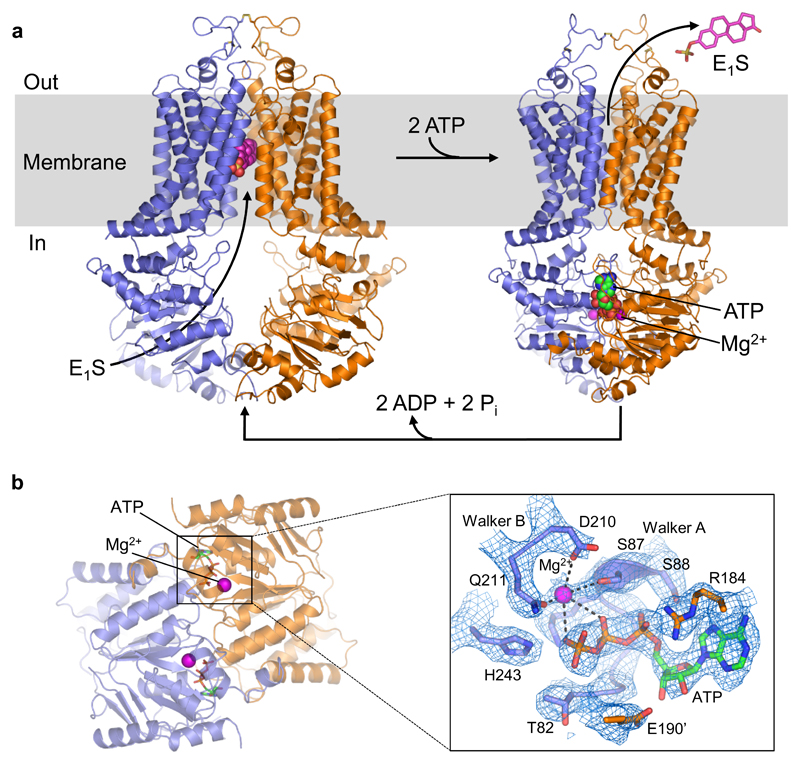
Figure 1. Structures and transport cycle of ABCG2.
a, Cartoon representation of E1S-bound ABCG2EQ (left) and ATP-bound ABCG2EQ (right). ABCG2 monomers are coloured blue and orange. Bound E1S, ATP, and Mg2+ are shown as spheres. In the ABCG2EQ-E1S structure, bound 5D3-Fab was omitted for clarity. b, Structure of NBD dimer of the ATP-bound state, viewed from the cytoplasm, with bound ATP and Mg2+ ions shown as sticks and spheres, respectively. Insert (~150° rotation to the right and viewed from the membrane): EM density around bound ATP, with Walker-A, Walker-B, E190 of the signature motif and “switch” histidine shown as sticks and labeled, and Mg2+ shown as purple sphere.