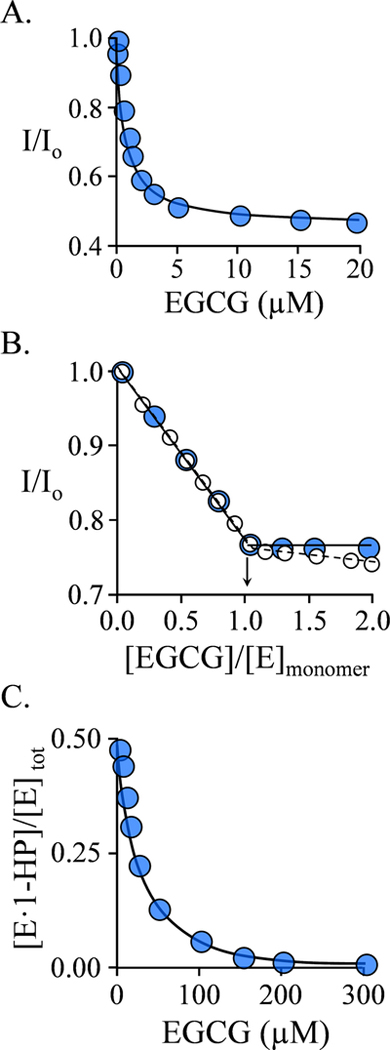
Figure 1. EGCG Binding Studies.
A.) Binding at the SULT1A1 Allosteric Site. Binding was monitored via changes in the intrinsic fluorescence of the enzyme (λex = 290 nm, λem = 370 nm). Fluorescence intensity is given relative to the intensity in the absence of ligand (I/I0). Conditions: SULT1A1 (0.25 μM, dimer), NaPO4 (50 mM), pH 7.5, 25 ± 2 °C. B.) Allosteric Site Binding Stoichiometry. Fluorescence measurements were as described in Panel A. Conditions: SULT1A1 (10 μM, monomer), E2 (0 μM (white dots), or 15 μM (26 ▪ Kd, blue dots)), NaPO4 (50 mM), pH 25 ± 2 °C. C.) Binding at the SULT1A1 Active Site. Binding was monitored via changes in the fluorescence anisotropy (λex = 385 nm, λem = 430 nm) of 1-HP — a competitive ligand. Conditions: SULT1A1 (6.0 μM, active site, 1.0 ▪ Kd 1-HP), 1-HP (10 μM, 1.5 ▪ Kd 1-HP), NaPO4 (50 mM), pH 7.5, 25 ± 2 °C. The fraction of enzyme-bound 1-HP was calculated from anisotropy measurements. For each titration, each point is the average of three independent determinations. The curves passing through the data in panels A and B are predicted by best-fit single-site and competitive-binding models, respectively. The stoichiometry was obtained from the point- of-intersection of the sub- and super-stoichiometric regions of the binding curve. All data were corrected for EGCG inner filter effects (see Materials and Methods).