Figure 4.
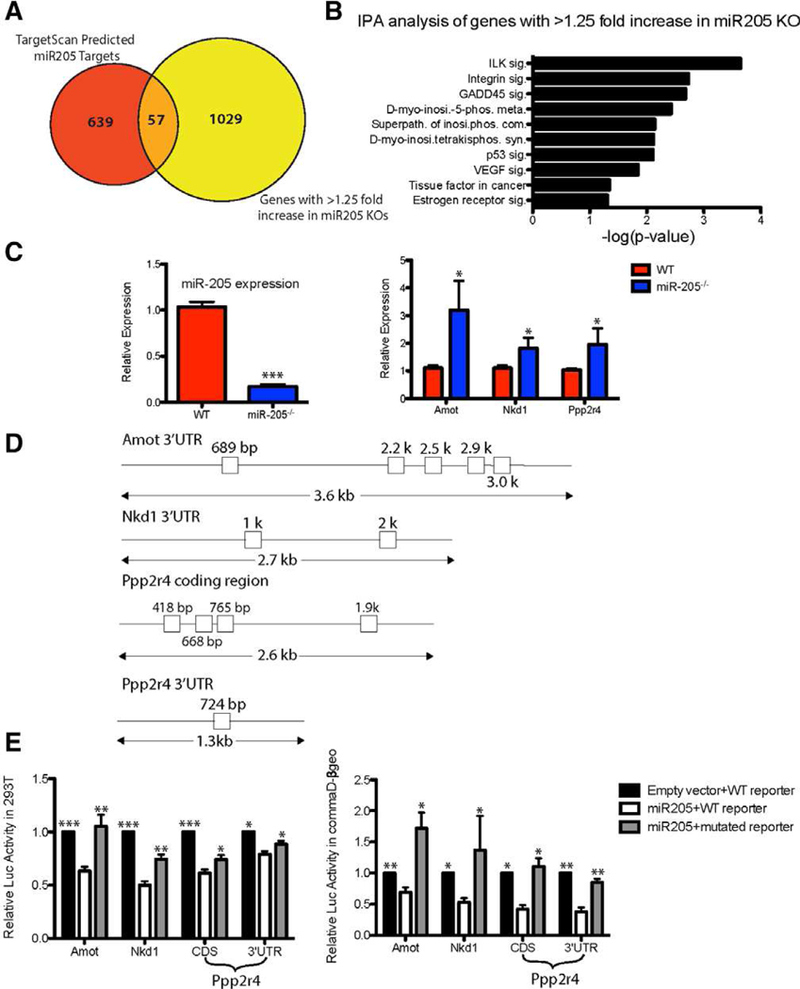
miR-205 targets negative regulators of YAP and canonical Wnt pathway. (A): RNA-seq identified 1,086 genes whose expression increased greater than 1.25-fold in the miR-205 null outgrowths. Among these, 57 were target-scan predicted miR-205 direct targets. Amot and Nkd1 were the top two targets on the list (see Supporting Information Table S1). (B): IPA analysis of the 1,086 genes whose expression increased greater than 1.25-fold in miR-205 null outgrowths. Ppp2r4 was a major component of multiple pathways, including ILK, D-myo-inositol-5-phosphate metabolism, integrin, and GADD45 signaling (also see Supporting Information Table S2). (C): Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) confirmation of miR-205 deletion as well as targets (Amot, Nkd1, and Ppp2r4) derepression in short culture of primary WT;RosamTmG/mTmG cre+ and miR-205fl/fl;RosamTmG/mTmG cre+ MECs. (D): Seed sequences present in the 30UTR of Amot, Nkd1, Ppp2r4 and the CDS of ppp2r4. (E): 30UTR of potential targets were cloned into a luciferase reporter and the luciferase activity was measured with WT and mutated miR-205 target sites. Luciferase activity was significantly decreased when miR-205 was cotransfected with WT seed sequences in 293T cells and commaDβ-geo cells. Mutations generated in each of the seed sequences significantly restored the luciferase activity. *p < .05; **p < .01; ***p < .001 by unpaired Student’s t tests.
