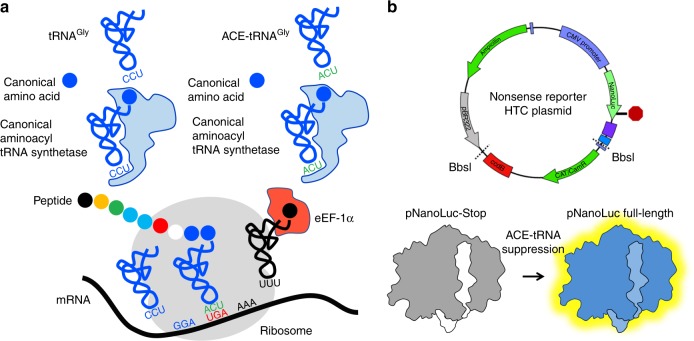
Fig. 1.
A nonsense mutation suppression screen to identify candidate anticodon edited tRNAs (ACE-tRNAs). a Schematic illustrates requisite interactions of ACE-tRNAs with translational machinery. Following delivery, ACE-tRNAs are recognized by an endogenous aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (blue shape) and charged (aminoacylated) with their cognate amino acid (blue circle). The aminoacylated ACE-tRNA is recognized by the endogenous elongation factor 1-alpha (red shape), which protects the ACE-tRNA from being de-acylated and delivers the aminoacyl ACE-tRNA to the ribosome (light gray shape) for suppression of a premature termination codon, in this instance UGA. b Individual ACE-tRNAs were cloned into the high throughput cloning nonsense Reporter plasmid using Golden Gate paired with CcdB negative selection. The all-in-one plasmid contains the NLuc luciferase reporter with either a UGA, UAG, or UAA PTC at p.162 between the enzymatic large bit and requisite C-terminal small bit