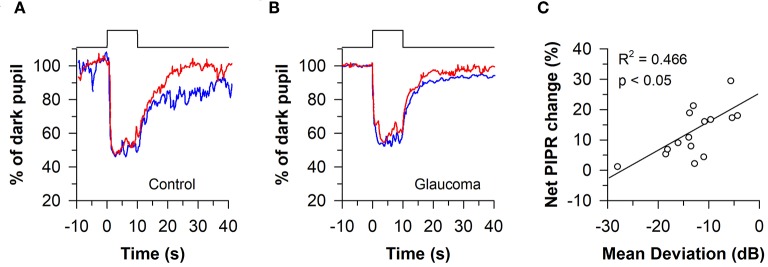
Figure 7.
Protocol for assessing melanopsin-dependent pupillary responses using the post-illumination pupillary light response (PIPR). The PIPR was assessed after exposure to 10 s of bright blue light or red light (488 or 610 nm; 14.2 log quanta/cm2/s). (A) In individuals with normal vision, the PIPR to blue light was greater than the PIPR to red light for at least 30 s after light offset. (B) In patients with glaucoma, the PIPR to blue light was reduced relative to red light, indicating reduced light transmission from melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells. (C) In glaucomatous eyes, the net PIPR change (the difference in the PIPR to blue light vs. red light, adjusted for baseline pupil size) correlated with visual field loss assessed by Humphrey visual field mean deviation. Panels (A,B) are redrawn with permission from (87). Panel (C) is redrawn with permission from (86).