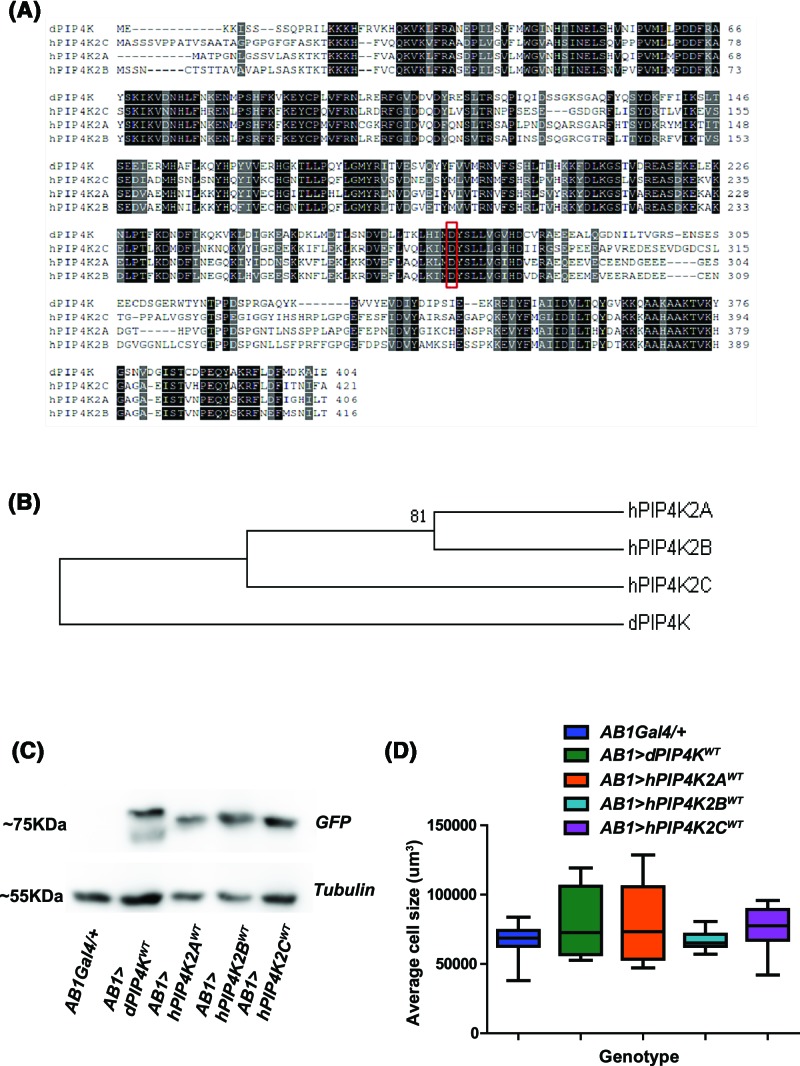
Figure 2. Heterologous expression of mammalian PIP4Ks in Drosophila cells and tissue.
(A) Protein alignment of the three human PIP4Ks against dPIP4K protein sequence. The conservation of residues has been marked from 60 to 80% (grey to black). The aspartic acid residue (D in the functional motif ‘MDYSLL’) has been marked with red box. (B) Phylogenetic tree representing the evolutionary distance between different PIP4Ks are used in the present study. The neighbour joining mode in MEGA 6 has been used to obtain the phylogenetic tree. The tree is represented at 50% consensus. The node with bootstrap value above 75% has been marked. (C) Protein levels in salivary glands of wild-type larvae overexpressing dPIP4K or the three human PIP4Ks as compared with AB1Gal4/+ probed for GFP tag on Western blot. Tubulin is used as a loading control. (D) Graph representing average cell size measurement (μm3) as mean ± S.E.M. of salivary glands from wandering third instar larvae expressing dPIP4KWT, hPIP4K2AWT, hPIP4K2B WT and hPIP4K2CWT in salivary glands as compared with AB1Gal4/+. n=5, no significant change was observed when analysed by unpaired t test.