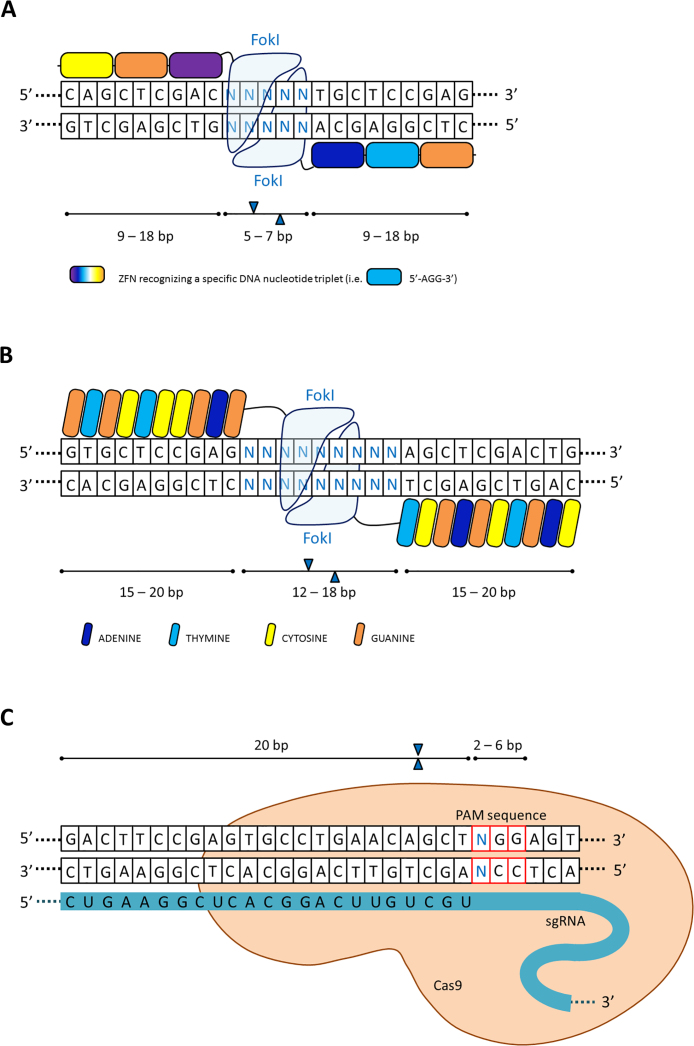
Fig. 1.
The construction of site-specific nuclease systems. (A) Zinc Finger Nucleases are hybrid proteins composed of zinc-finger arrays (3–6 ZFNs in each hybrid protein) and the catalytic domain of FokI endonuclease. Each ZFN subunit recognizes and binds to a specific DNA nucleotide triplet in the target sequence. Dimerization of the FokI catalytic domain leads to the formation of double-strand breaks (DSBs). (B) TALEN are hybrid proteins composed of TAL effector DNA-binding domain arrays (15–20 TALE subunits in each TALEN protein) and the catalytic domain of FokI endonuclease. One monomer of TALE recognizes one nucleotide of a target DNA sequence. Dimerized FokI endonuclease introduces a double-strand break into DNA sequence. (C) The CRISPR/Cas9 two-component system is composed of Cas9 endonuclease and the single-guide RNA (sgRNA) molecule (20 base pair long). Cas9 endonuclease domains cleave both strands within the target sequence preceding the protospacer-associated motif (PAM) NGG trinucleotide sequence. bp – base pair; FokI – endonuclease FokI.