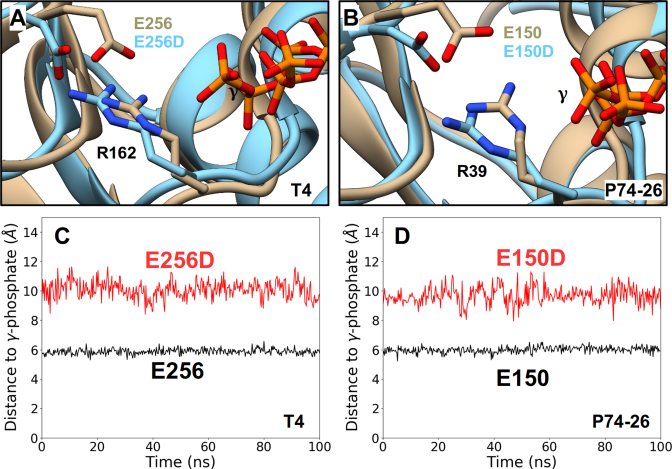
Figure 7.
Effects of the Conservative ASCE E→D Mutation Obtained from MD Simulations. Representative conformations of the ATP-binding pocket of ATP-bound WT TerLs (tan) superimposed onto the binding pocket conformations of the corresponding catalytic E→D mutant TerLs (cyan). Such analysis carried out for TerLT4 (A) and TerLP74-26 (B) structures show significant displacement of the labeled carboxylate functional group and miscoordination of the labeled γ-phosphate of ATP in both mutant structures. Separation distances, obtained from an equilibrium MD trajectory, between the carboxylate functional group and the γ-phosphate for WT (black) and catalytic E→D mutants (red) of TerLT4 (C) and TerLP74-26 (D). In both cases, the E→D change results in a significant increase this distance and the hindered ATP hydrolysis observed experimentally in the E→D mutants is attributed to this increased distance.