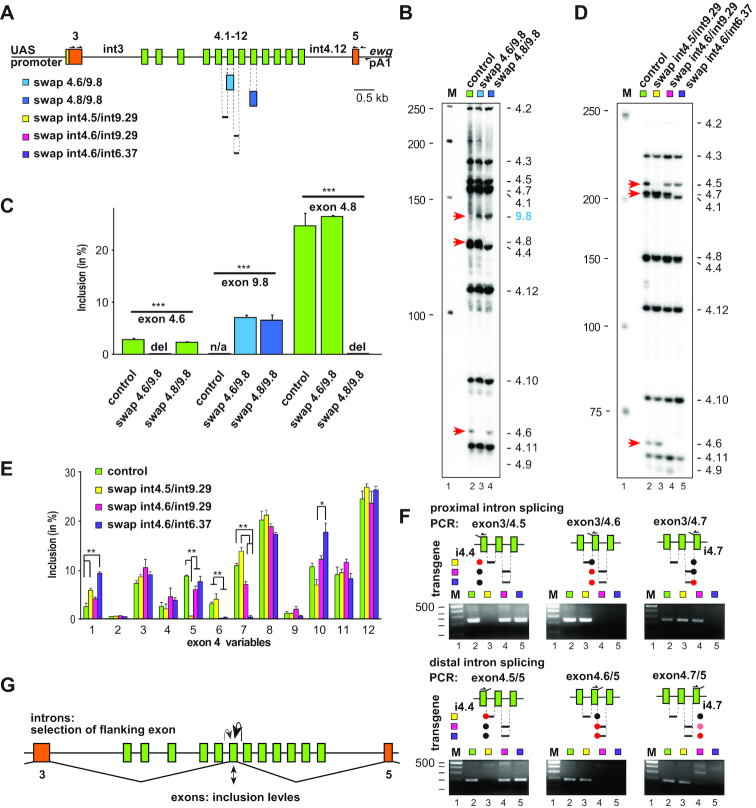
Figure 6.
Exon and intron sequences determine inclusion levels in the Dscam exon 4 cluster (A) Schematic of the pUC 3GLA HAi Dscam 3–5 depicting transgenes ‘swap 4.6/9.8’ (light blue) and ‘swap 4.8/9.8’ (dark blue) where exon 4.6 or 4.8 was exchanged with exon 9.8, respectively. ‘Swap int4.5/int9.29’ (black line), ‘swap int4.6/int9.29’ (black line) and ‘swap int4.6/int6.37’ (grey line) indicate transgenes with accordingly exchanged introns. (B) Denaturing acrylamide gel showing inclusion of individual exon 4 variable exons from neuronal expression with elavGAL4 in third instar larval brains from construct specific nested RT-PCR and identification by restriction digests (MboI, AluI, HinPI and TaqI) from control (Dscam 3–5, green, lane 2), the exchange of exon 4.6 with exon 9.8 (swap 4.6/9.8, light blue, lane 3) and exon 4.8 with exon 9.8 (swap 4.8/9.8, dark blue, lane 4) transgenes. Red arrowheads point towards absent exons and the blue arrowhead points towards exon 9.8 swapped for exon 4.6 or 4.8, respectively. (C) Quantification of inclusion levels for exons 4.6, 4.8 and 9.8 in the control (Dscam 3–5), swap 4.6/9.8 and swap 4.8/9.8 transgenes shown as means with standard error from three experiments. Statistically significant differences are indicated above bars (**P < 0.001). (D) Denaturing acrylamide gel showing inclusion of individual exon 4 variable exons from neuronal expression with elavGAL4 in third instar larval brains from construct specific nested RT-PCR and identification by restriction digests (MboI, AluI, HinPI and TaqI) from control (Dscam 3–5, green, lane 2), the exchange of intron 4.5 with intron 9.29 (swap int4.5/int9.29, yellow, lane 3), intron 4.6 with intron 9.29 (swap int4.6/int9.29, magenta, lane 4) and intron 4.6 with intron 6.37 (swap int4.6/int6.37, purple, lane 5) transgenes. Red arrowheads point towards absent exons. (E) Quantification of inclusion levels for exons 4.1 to 4.12 in control (Dscam 3–5, green), swap int4.5/int9.29 (yellow), swap int4.6/int9.29 (magenta) and swap int4.6/int6.37 (magenta) transgenes shown as means with standard error from three experiments. Statistically significant differences are indicated above bars (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (F) Diagnostic PCR from cDNA of each transgene for splicing of the proximal (top) and distal (bottom) intron of indicated variable exons. Primers are indicated above exons and swapped introns below according to the color code: swap int4.5/int9.29 (yellow), swap int4.6/int9.29 (magenta) and swap int4.6/int6.37 (magenta). Black dots indicate productive splicing, pink dots weak splicing and red dots mark absent splicing. PCR products were separated on 3% agarose gels. One hundred base pair size markers are shown on the left. (G) Model for the regulation of mutually exclusive alternative splicing in the Dscam exon 4 cluster. Intron sequences between exon 4 variables are key to selection of preceding variable exons (black arrow), and to a lesser extent for selection of the following exon (grey arrow) as indicated on top of the gene model. Sequences within variable exons impact on their inclusion levels (double arrow, bottom).