Figure 2.
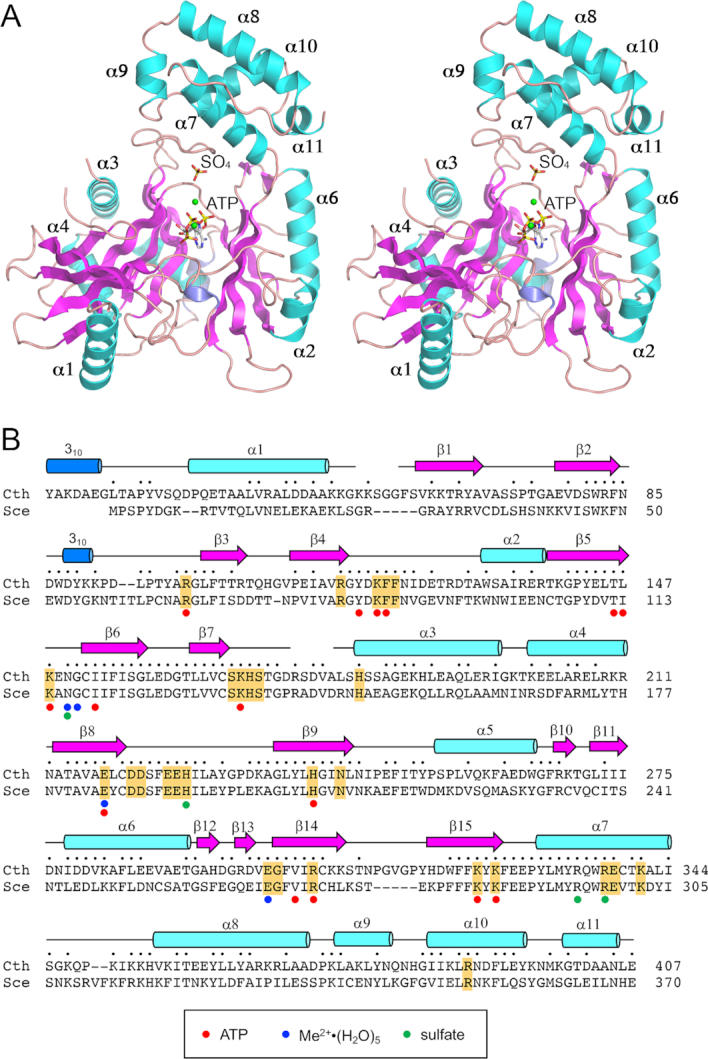
Structure of Trl1-LIG. (A) Stereo view of the LIG tertiary structure, depicted as a ribbon model with magenta β strands, cyan α helices (numbered sequentially), and blue 310 helices. The ATP in the active site and a nearby sulfate anion are rendered as stick models. Mn2+ ions are depicted as green spheres. (B) Secondary structure elements (colored as in panel A) are displayed above the C. thermophilum (Cth) Trl1-LIG primary structure, which is aligned to the primary structure of the LIG domain of S. cerevisiae (Sce) Trl1. Positions of amino acid side chain identity or similarity are indicated by dots above the Cth sequence. Gaps in the alignment are indicated by dashes. Amino acids in Trl1-LIG that make atomic contacts to ATP are denoted by red dots below the alignment. Amino acids that coordinate the hydrated metal complex are indicated by blue dots below the alignment. Amino acids that coordinate the sulfate anion are indicated by green dots below the alignment. The amino acids in S. cerevisiae Trl1-LIG that were identified by alanine scanning as essential for LIG activity in vivo (6) are highlighted in gold shading.
