Figure 3.
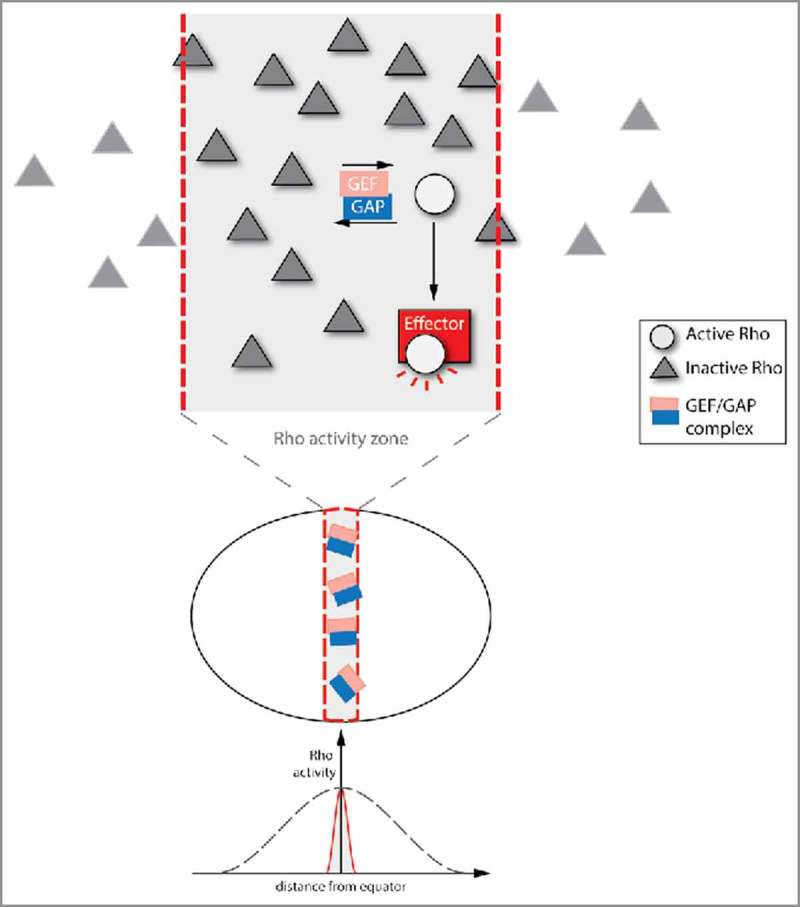
Cycling between Rho GTPase inactivation and activation creates a restricted Rho activity zone. The Rho activity cycling that emerges from spatially and temporally overlapping GAP and GEF activities can create spatially defined Rho activity zones. In this model, the Rho GTPase is only activated by a GEF within a specific part of the cell. The active form of the Rho GTPase is anchored in the Rho activity zone by the GAP, which is also area-specific (or even in a complex with the GEF). GAP-bound active Rho GTPase is immediately inactivated, leading to constant cycling between active and inactive states. However, effectors can bind to the active form of the Rho GTPase, and thereby enable downstream Rho signaling. This type of spatial restriction is necessary for successful cytokinesis in the Xenopus embryo.
