Figure 4.
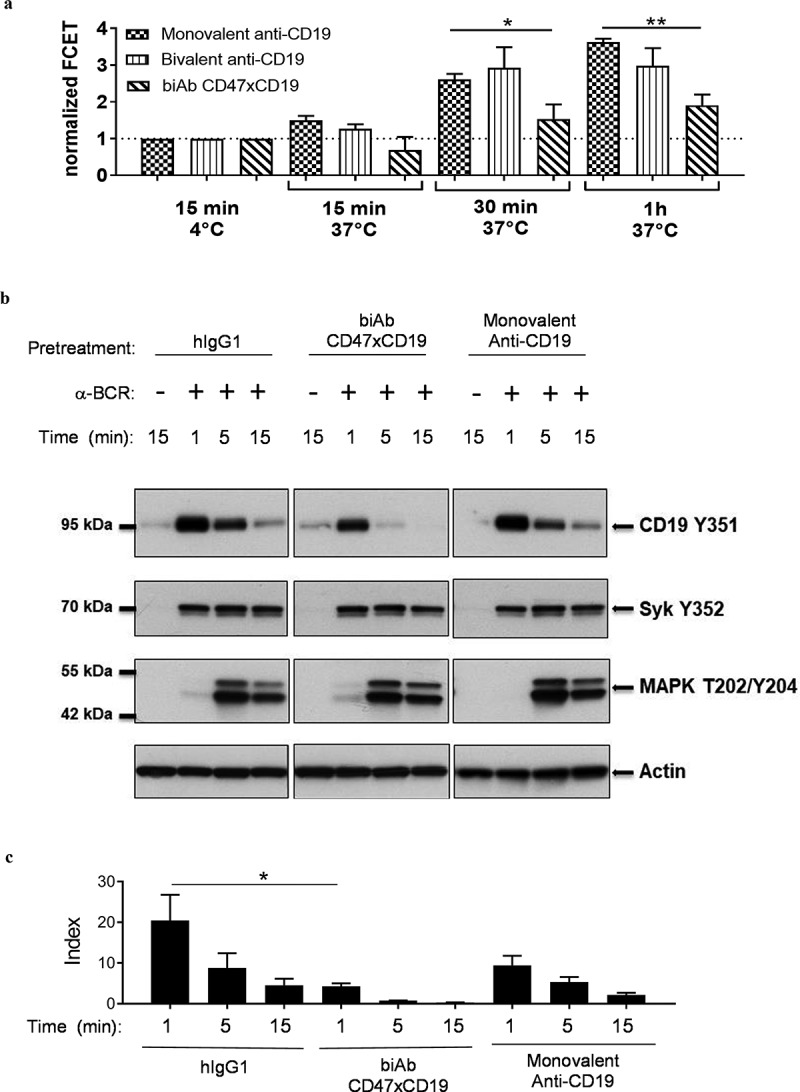
CD47/CD19 co-engagement interferes with CD19 migration to the BCR and impairs CD19 phosphorylation upon BCR cross-linking.
(a) Ramos B cells were incubated with equimolar amount of Cy3-labeled anti-BCR (e.g., anti-IgM) and Cy5-labeled monovalent or bivalent anti-CD19 or anti-CD47xCD19 biAb (15 min, 30 min or 1 hour, 37°C) before being washed and analyzed for FRET by flow cytometry. Data are presented as normalized FCET where the FCET values obtained for each Cy3/Cy5 pair of antibodies incubated at 4°C were set at 1 defining a threshold (dashed line) above which a sample is considered positive for targets clustering. Graph represents the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. (b, c) Ramos B cells were serum-starved for 5 hours and pretreated with 10 μg/mL of hIgG1 isotype control, anti-CD47xCD19 biAb or monovalent anti-CD19 (15 min, RT) before activation by BCR-crosslinking with an anti-IgM for the indicated time points at 37°C. Cell lysates were fractioned by SDS-PAGE and transferred onto nitrocellulose for subsequent immunoblotting to assess phosphorylation of CD19-Y531, Syk-Y352 and MAPK (Erk1/Erk2)-T202/Y204. Actin is used as a control of protein loading. (b) One representative western blot experiment from three independent ones is shown. (C) The ratio of phospho- CD19-Y531 over actin signal intensities were calculated and converted to index relative to unstimulated B cells. Data show mean index ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using the one way ANOVA test: *p < 0.05.
