Figure 5.
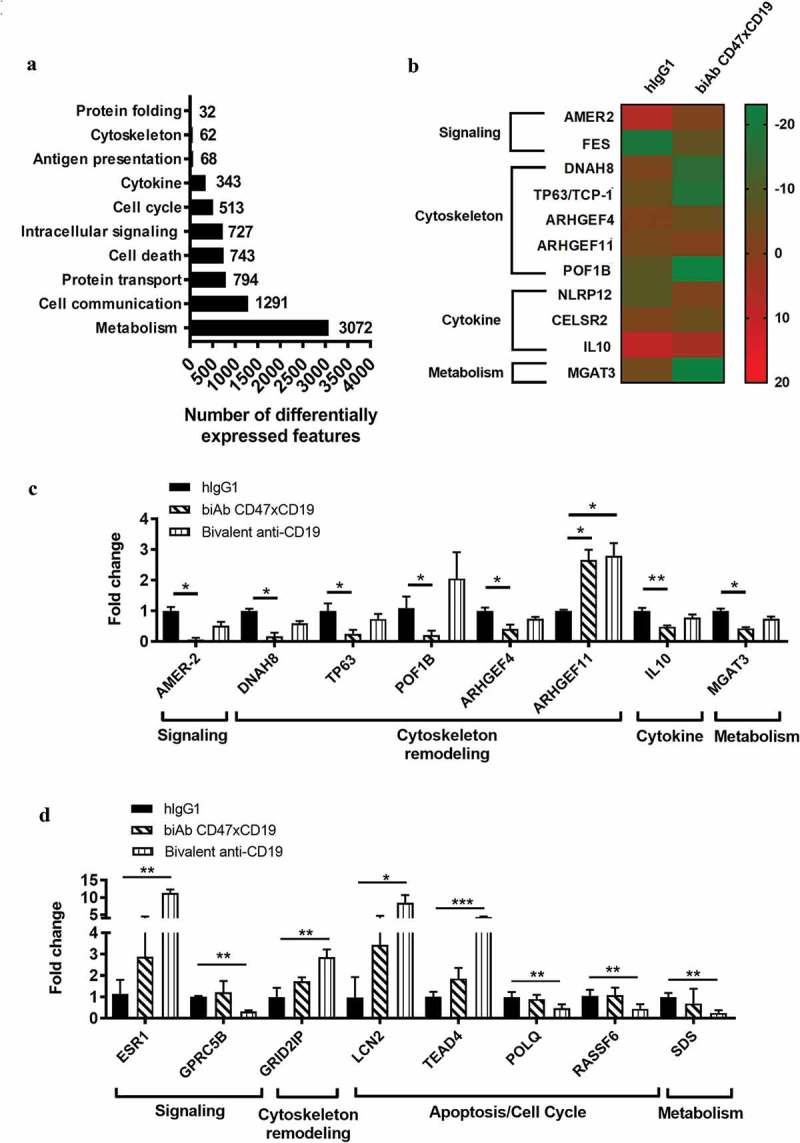
BCR-induced gene expression changes in response to CD47xCD19 co-engagement.
Purified human primary B cells were pretreated (15 min, RT) with 10 μg/mL hIgG1 isotype control, anti-CD47xCD19 biAb or bivalent anti-CD19 and then stimulated with 5 μg/mL anti-BCR and 1 μg/mL anti-CD40 antibodies. After incubation (4 hours, 37°C), total RNA were isolated for subsequent investigation by RNA sequencing. (a). Number of differentially expressed features and their functional classification identified in response to BCR stimulation. (b) Heatmap of the genes differentially expressed between the hIgG1-treated group and anti-CD47xCD19 biAb-treated group. The color key represents fold of induction of each gene over the unstimulated control. Genes are classified according to their biological function. (c) Relative expression levels of the genes differentially expressed between the hIgG1-treated group and the anti-CD47xCD19 biAb-treated group or (d) the bivalent anti-CD19 mAb-treated group. The values were normalized to the mean expression level in the hIgG1-treated group, which was arbitrarily set as 1. Data shown are the mean values ± SEM of each gene from three B cell donors. Statistical analysis was performed using the paired T test: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.05.
