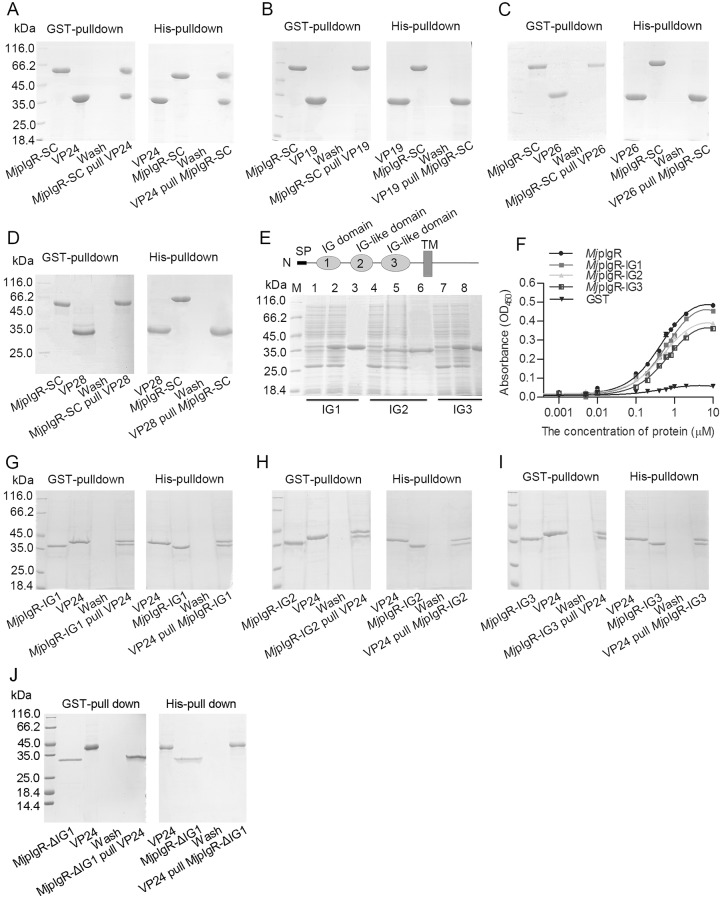
Fig 6. MjpIgR binds to WSSV via its IG-like domains.
A, The interaction of MjpIgR-SC with VP24 was analyzed using GST- and His-Pulldown assays. B, The interaction of MjpIgR-SC with VP19 was detected by GST- and His-Pulldown assays. C, GST- and His-Pulldown to analyze interactions of MjpIgR-SC with His-VP26. D, GST- and His-Pulldown to detect interactions of MjpIgR-SC with VP28. E, Recombinant expression and purification of IG1, IG2, and IG3 from MjpIgR. Constructs pGEX4T-1-MjpIgR-IG1, 2, or 3 were transformed into E. coli, and the expression of IG1-3 was induced by IPTG and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Lanes 1, 4, and 7, total proteins from E. coli with pGEX4T-1-MjpIgR-IG1, IG2, and IG3 without IPTG induction; lanes 2, 5, and 8, total proteins from the E. coli with IPTG induction; lanes 3, 6, and 9, purified recombinant MjpIgR-IG1, -IG2, and IG3 proteins; lane M, protein molecular mass standard. F, ELISA assay to detect the binding of MjpIgR to WSSV. (G-I) Each of the IG domains (IG1–3) was used in a pulldown assay, including GST pulldown (left panel) and His pulldown (right panel) to detect the interaction of the IG domains with VP24. J, Truncating mutation of IG1 domain of MjpIgR and its interaction with VP24 of WSSV analyzed by GST and His pulldown assays.