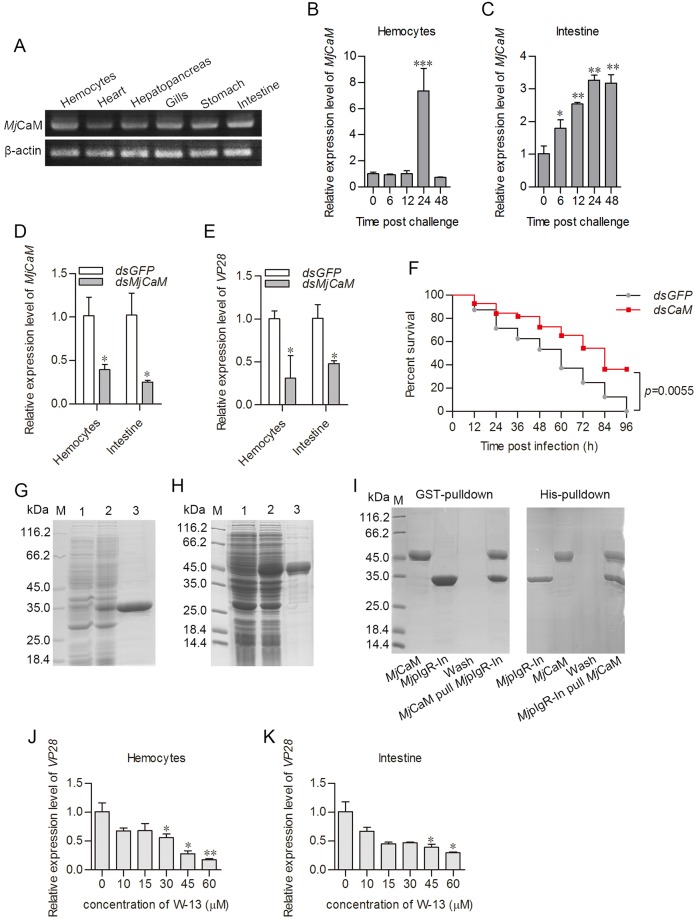
Fig 7. Calmodulin interacts with MjpIgR-In and is involved in WSSV endocytosis.
A, The tissue distribution of MjCaM mRNA. B, C, Expression levels of MjCaM in hemocytes and intestine, as detected by qPCR after WSSV infection. D, Efficiency of RNA interference of MjCaM in hemocytes and intestine. E, The vp28 expression levels in dsGFP and dsMjCaM groups after WSSV challenge. F, Survival rates after WSSV infection in different interference groups. Significant differences were analyzed using the software GraphPad Prism 5.0. G, H, MjpIgR-In and MjCaM expression and purification from E. coli. Lane 1, total proteins from E. coli with pET32a-MjpIgR-In or pGEX4T-1-MjCaM without IPTG induction; lane 2, total proteins from the E. coli with IPTG induction; lane 3, purified recombinant MjpIgR-In or MjCaM protein. I, Interactions between His-tagged MjpIgR-In and GST-tagged MjCaM were detected using pull-down assays. J, K, Expression level of vp28 in hemocytes and intestine treated with different concentrations of W-13. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.