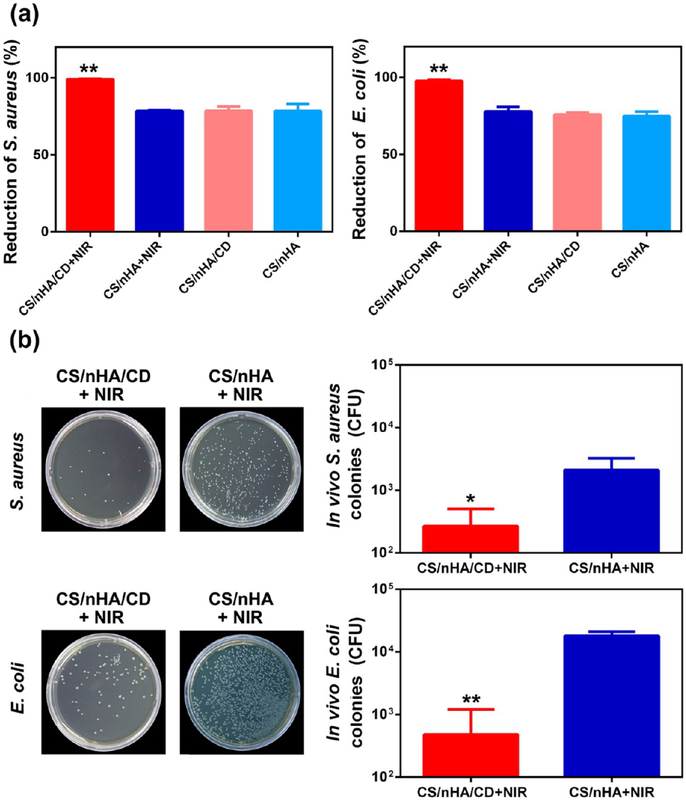
Figure 8.
Antibacterial properties of the scaffolds. (a) In vitro antibacterial rate against clinically relevant S. aureus (left) and E. coli (right) of the different groups. The CS/nHA/CD+NIR group showed significantly higher antibacterial activity against clinical bacteria. (b) Number of clinically relevant S. aureus (top) and E. coli (bottom) bacterial colonies after bacteria from the harvested samples was cultured for 24 h after 1 week treatments in vivo. Each value is the mean ± standard deviation; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.