Figure 4.
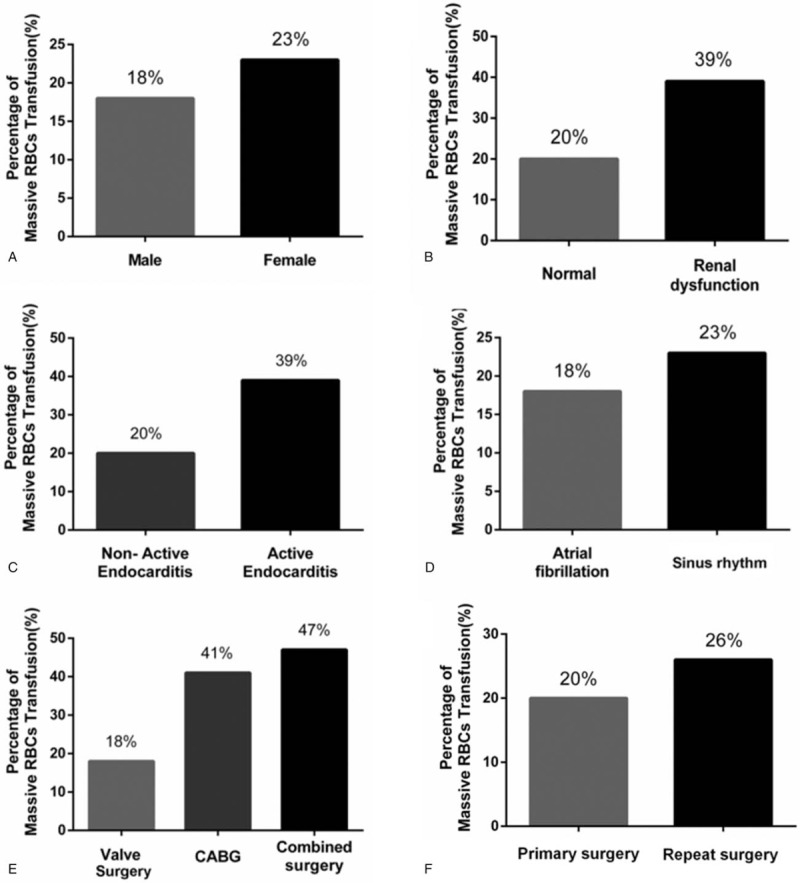
Effect of (categorical) risk factors on massive red blood cell transfusion (MRT). Incidence of MRT was 5% lower among men than women (A) and 5% lower among patients with atrial fibrillation than among those without it (B). MRT incidence nearly doubled in the presence of renal dysfunction (C), in the presence of active endocarditis (D), or when the surgery involved coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or the combination of CABG and valve surgery (E). MRT incidence was higher among patients undergoing repeat surgery than among those undergoing primary surgery (F).
