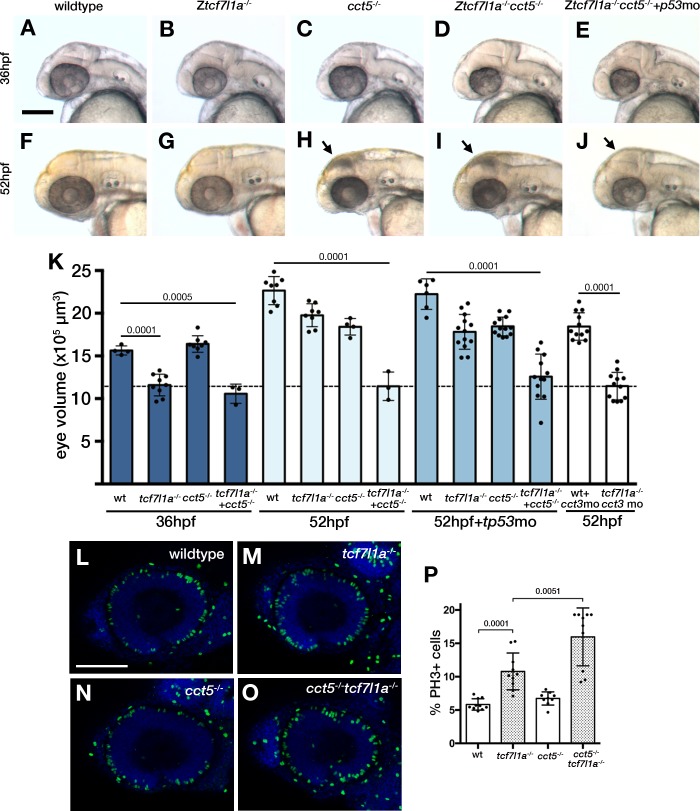
Figure 8. Loss of tcf7l1a modifies the cct5u762 mutant eye phenotype.
(A–J) Lateral views of wildtype (A, F), Ztcf7l1a-/- mutant (B, G) cct5U762/u762 mutants (C, H), double cct5U762/u762/Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants (D, I) and double cct5U762/u762/Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants injected with 0.8 pmol of cct3 morpholino (E, J) at indicated stages. Scale bar = 100 µm. Full data in Supplementary file 10O, single experiment, 36hpf, wt n = 4, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 9, cct5-/- n = 8, cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 3; 52hpf, wt n = 8, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 8, cct5-/- n = 4, cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 3; 52hpf + 2 pmol tp53 morpholino, wt n = 6, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 13, cct5-/- n = 13, cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 12; 52hpf + 0.8 pmol cct3 morpholino, wt n = 12, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 12. (K) Eye volume quantification at the indicated timepoints and conditions shown in A–J) (data in Supplementary file 1O). Unpaired t-test. (L–O) Immunostaining detecting phosphohistone3 (PH3, green) in wildtype (L), Ztcf7l1a-/- (M), cct5-/- (N), cct5-/-/Ztcf7l1a-/- (O) eyes at 32hpf. (P) Plot showing the percentage of PH3 positive cells in the eyes shown in L–O) (data in Supplementary file 1Q) Single experiment, wildtype n = 10, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 10, cct5-/- n = 9, cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/-n = 10, unpaired t-tests.
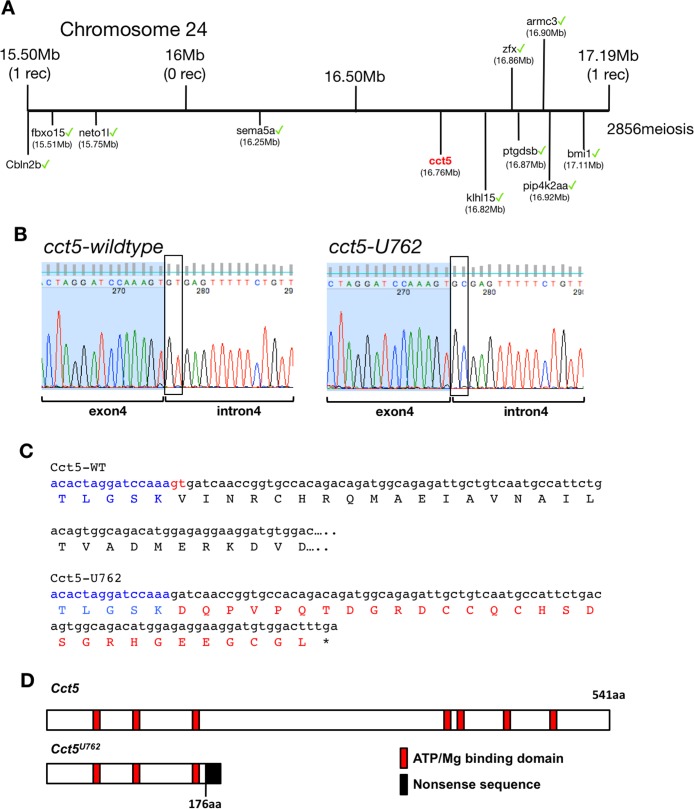
Figure 8—figure supplement 1. Genetic mapping of U762 and description of the cct5U762 mutation.
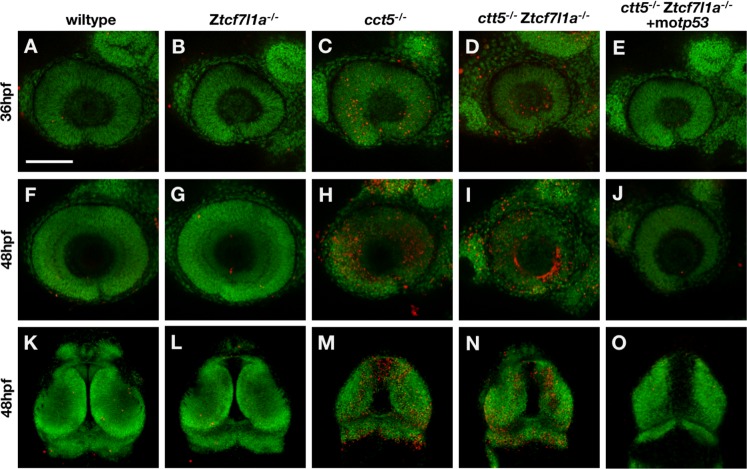
Figure 8—figure supplement 2. Whole mount Tunel cell death analysis in cct5/tcf7l1a mutants.
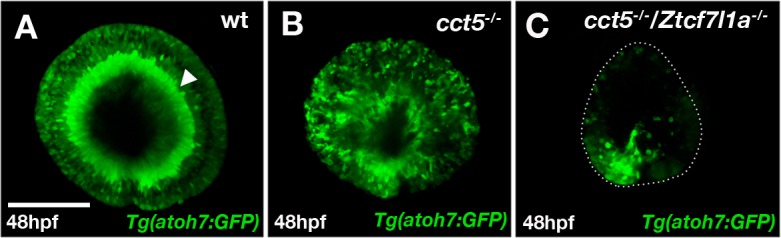
Figure 8—figure supplement 3. atoh7 expression in cct5/tcf7l1a mutants.