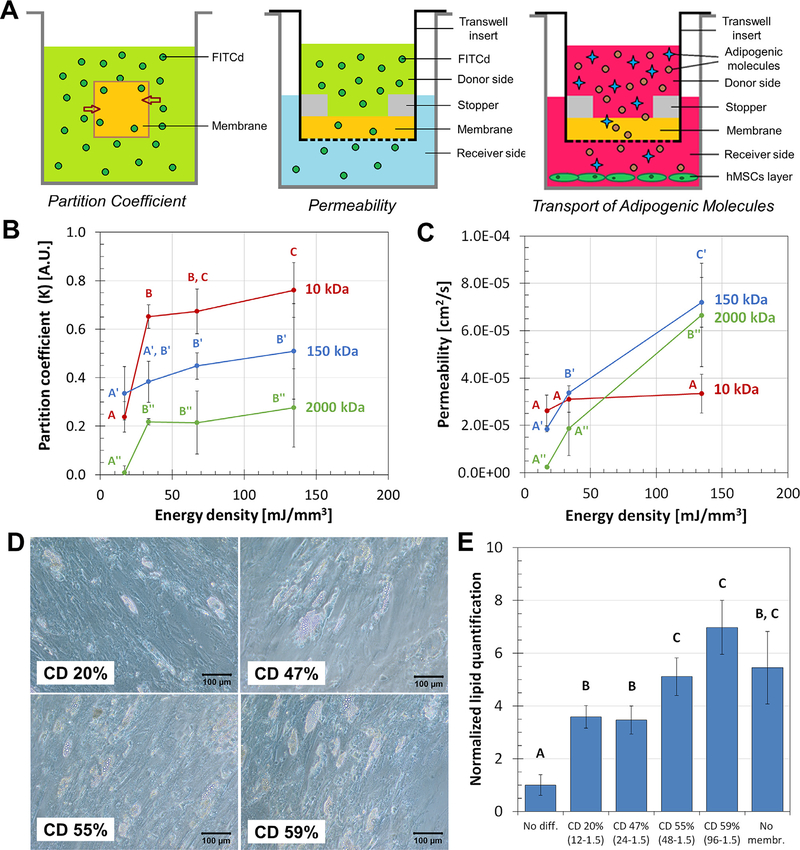
Fig. 4.
The effects of crosslink degree (CD) on transport phenomena across keratin membranes. A) Transport phenomena across the keratin membranes were studied using simplified models of the partition coefficient, permeability, and diffusion transport of adipogenic molecules. B) The partition coefficient of keratin hydrogels in equilibrium state with 10, 150, and 2000 kDa FITCd solutions; ED had greater significant effect on the coefficient for smaller molecules. C) Permeability, on the other hand, is the dynamic interaction of the gel with the solute and was affected by ED for the high MW molecules. D-E) Adipogenic differentiation of hMSCs was significantly affected by the variation of the CD of the membranes used. Imaging and quantification of intracellular lipids determined that membranes with higher CD allow better transport of nutrients and adipogenic molecules after 28 d. For all plots, samples that do not share the same letter are significantly different (p < 0.05).