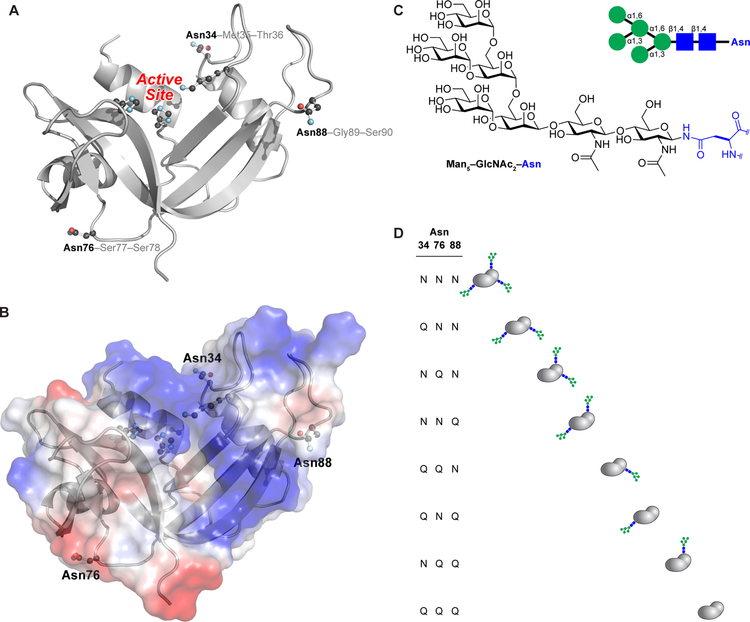
Figure 1.
Three-dimensional structure of human RNase 1. (A) The side chains of the asparagine residues within N-glycosylation sequons (Asn34, Asn76, and Asn88) and the active-site residues (His12, Lys41, and His119) are shown explicitly. The image was created with Protein Data Bank entry 1z7x, chain Z22 and the program PyMOL from Schrödinger (New York, NY). (B) Electrostatic potential map of the surface of human RNase 1. The image was created as in Figure 1A. (C) Structure of the core heptasaccharide, Man5GlcNAc2, that is appended to asparagine residues. (D) Macroscopic glycoforms of human RNase 1 generated by strategic asparagine→glutamine substitution. The three-letter shorthand is used to name each variant.