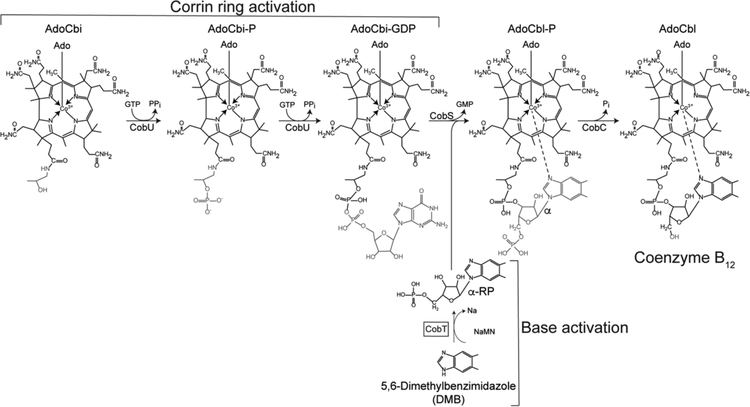
Figure 3. Late steps of coenzyme B12 biosynthesis.
This figure schematizes the two branches of the nucleotide loop assembly (NLA) pathway that yields coenzyme B12 in S. enterica. This bacterium can assimilate exogenous, incomplete corrinoids such as cobinamide (Cbi) converting it to AdoCbi and activating it to AdoCbi-GDP via AdoCbi-P using the bifunctional kinase/guanylyltransferase (CobU) enzyme. The base shown in this scheme is 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole (DMB), which is activated to its α-ribotide by the CobT PRTase (shown inside the box). Condensation of the activated intermediates followed by dephosphorylation yields biologically active coenzyme B12.