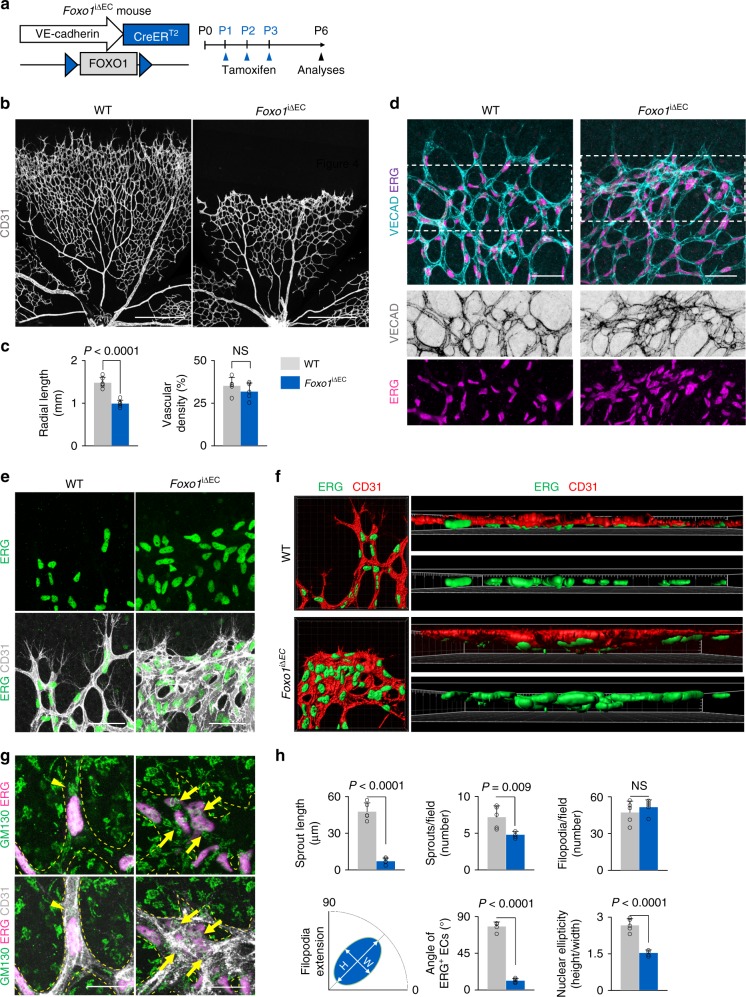
Fig. 4.
FOXO1 is required for establishing endothelial polarization. a Diagram depicting the experiment schedule for EC-specific deletion of FOXO1 in retinal vessels from P1 and their analyses at P6. b, c Images of CD31+ vessels and comparisons of indicated parameters in WT (n = 5) and Foxo1i∆EC (n = 5) mice. Scale bar, 500 μm. d Images showing VECAD and ERG+ nuclei of ECs at the vascular front of WT and Foxo1i∆EC mice. Middle and bottom panels show VE-cadherin (VECAD) and ERG signals of insets (dashed-line boxes) in top panels. Scale bars, 100 μm. e Magnified images of CD31+ vessels and ERG+ nuclei of ECs. Scale bars, 50 μm. f 3D reconstructed images of CD31+ vessels and ERG+ nuclei of ECs in WT and Foxo1i∆EC mice. g Images of CD31+ vessels, ERG+ nuclei of ECs and GM130+ Golgi apparatus at tip ECs in WT and Foxo1i∆EC mice. The yellow dashed line outlines CD31+ vessels. Note that GM130+ Golgi apparatus are polarized towards the anterior or posterior of the nuclei in tip ECs of WT mice (yellow arrowheads), while such polarization is lost in tip ECs of Foxo1i∆EC mice (yellow arrows). Scale bars, 20 μm. h Comparisons of indicated parameters in WT (n = 5) and Foxo1∆EC (n = 5) mice. Data represent mean (bar) ± s.d. (error bars). p values, versus WT by two-tailed unpaired t-test. NS not significant. Source data are provided as a Source Data file