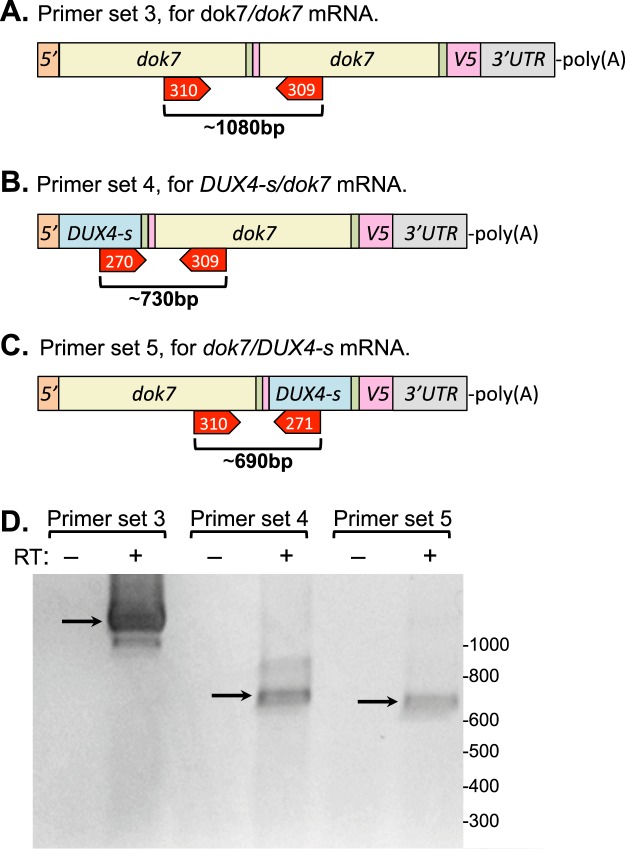
Figure 8.
Identification of mRNAs generated by trans-splicing of DUX4-s and dok7 mRNAs. (A) Diagram of primer set 3 (primers #310 and #309) designed to generate a RT-PCR product of ~1080 bp from trans-spliced mRNA containing two sequential dok7 coding sequences. (B) Diagram of primer set 4 (primers #270 and #309) designed to generate a RT-PCR product of ~730 bp from trans-spliced mRNA in which the DUX4-s coding sequence is upstream of (5′ to) the dok7 coding sequence. (C) Diagram of primer set 5 (primers #310 and #217) used to identify an alternative configuration of the trans-spliced mRNA in which dok7 is upstream of (5′to) DUX4-s. (D) All three sets of primers generated reverse transcriptase (RT) dependent bands of the expected sizes (arrows), indicating that all forms of the trans-spliced mRNAs were generated. Sequencing of the bands indicated by arrows confirmed that trans-splicing joined the donor 1 site in the V5 epitope sequence of one mRNA to the upstream acceptor 1 site in the 5′ region of the second mRNA, exactly as seen above for trans-splicing of two DUX4-s mRNAs, i.e., as in band “B” of Figs 5 and 6A,B.