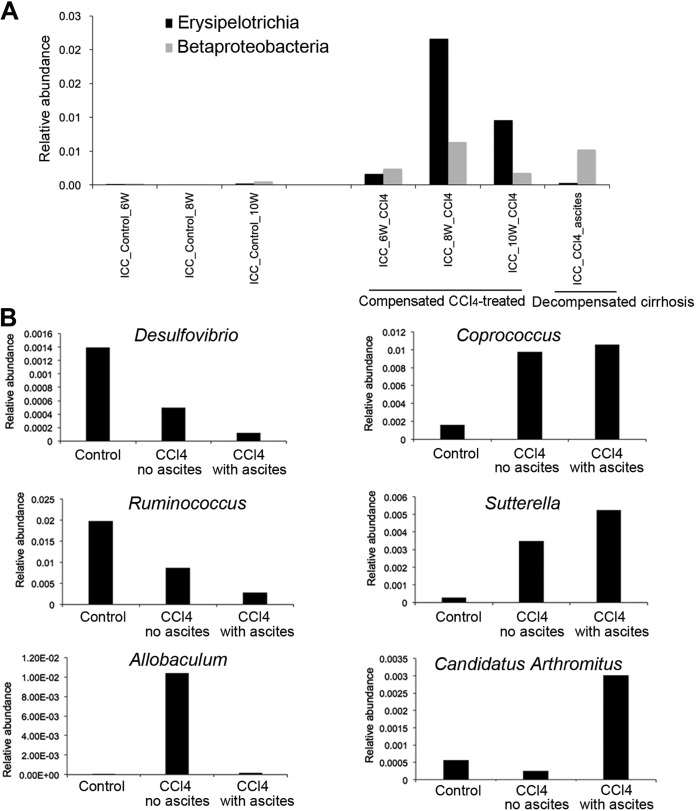
FIG 2.
Microbial groups in ileocecal contents (ICC) samples involved in the severity of cirrhosis. (A) Temporal taxonomic differences between controls and CCl4-treated rats. Two classes of bacteria, Erysipelotrichia (P = 0.001, q = 0.012) and Betaproteobacteria (P = 0.01, q = 0.098), presented significantly different relative abundances over time between the control and the CCl4-treated groups. Statistics were performed using the Kruskal-Wallis test. (B) Taxonomic differences between controls and CCl4-treated rats with ascites and CCl4-treated rats before development of ascites. Two bacterial genera, Coprococcus (P = 0.0001, q = 0.011) and Sutterella (P = 0.0005, q = 0.014), were found in higher relative abundances in CCl4-treated rats than in control rats. Two bacterial genera, Desulfovibrio (P = 0.002, q = 0.025) and Ruminococcus (P = 0.0007, q = 0.013), were found in higher relative abundances in control rats than in CCl4-treated rats. Allobaculum was found in higher relative abundance (P = 0.0004, q = 0.013) only in compensated CCl4-treated rats, and “Candidatus Arthromitus” (P = 0.023, q = 0.15) was in higher relative abundance in decompensated cirrhotic rats. Statistics were performed using the Kruskal-Wallis test.