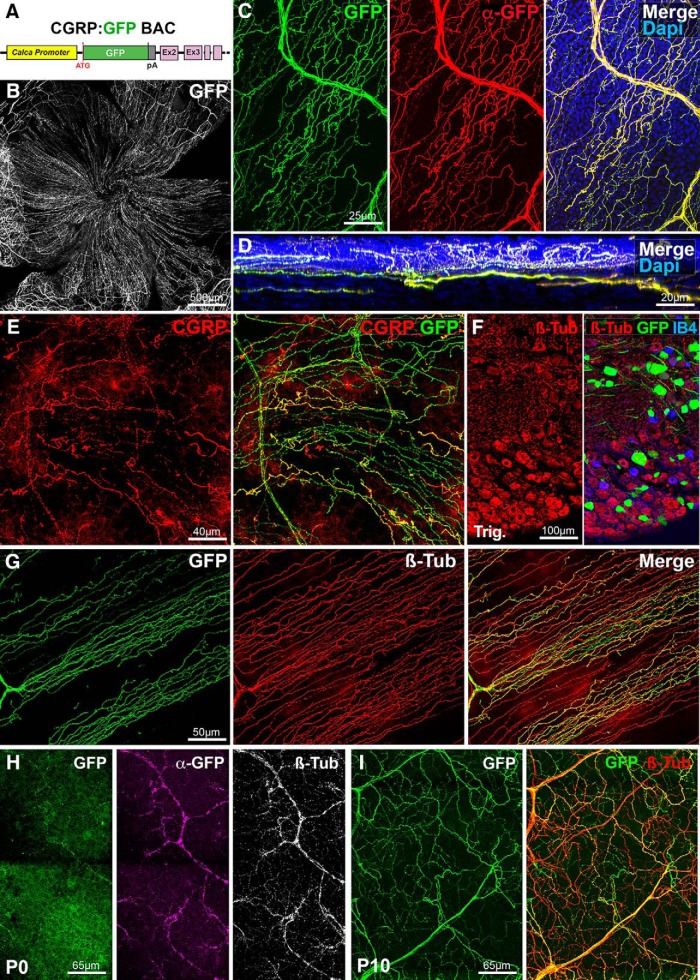
Figure 1.
Visualization of corneal peptidergic axons in CGRP:GFP mice. All panels (except D and F) are maximal intensity z-projection confocal stacks from whole-mount corneas. A, Schematic of the CGRP:GFP BAC transgenic construct. GFP was inserted downstream the promoter of the Calca gene, which encodes CGRP. B–G, Images from adult CGRP:GFP mice. B, Flat mount view of a whole-mount cornea, showing GFP expression in corneal nerves. C, Cornea immunolabeled with anti-GFP with DAPI counterstaining (blue). There is a perfect overlap (merge) between the endogenous GFP fluorescence (green) and the anti-GFP immunoreactivity (red). D, A reslice of the cornea (54-μm-thick optical section) showing the location of the GFP axons in the stroma, sub-basal plexus, and epithelium. E, Cornea immunolabeled with anti-CGRP (red). All CGRP axons are also GFP+. F, Cryostat section of the trigeminal ganglion stained with IB4 (blue) and immunolabeled for βIII-tubulin (red). GFP neurons only represent a subset of βIII-Tub+ trigeminal neurons. G, Cornea immunolabeled with anti-βIII-tubulin (red). Typical corneal axon leashes of almost parallel GFP+ axons (green) are seen. GFP is only expressed in a subset of corneal nerves. H, At P0, the endogenous GFP expression is weaker than after anti-GFP immunostaining (magenta). All corneal axons in this domain can be seen with anti-βIII-tubulin immunostaining (white, right). I, GFP+ axons in the P10 cornea immuno-labeled for βIII-tubulin.