Figure 4.
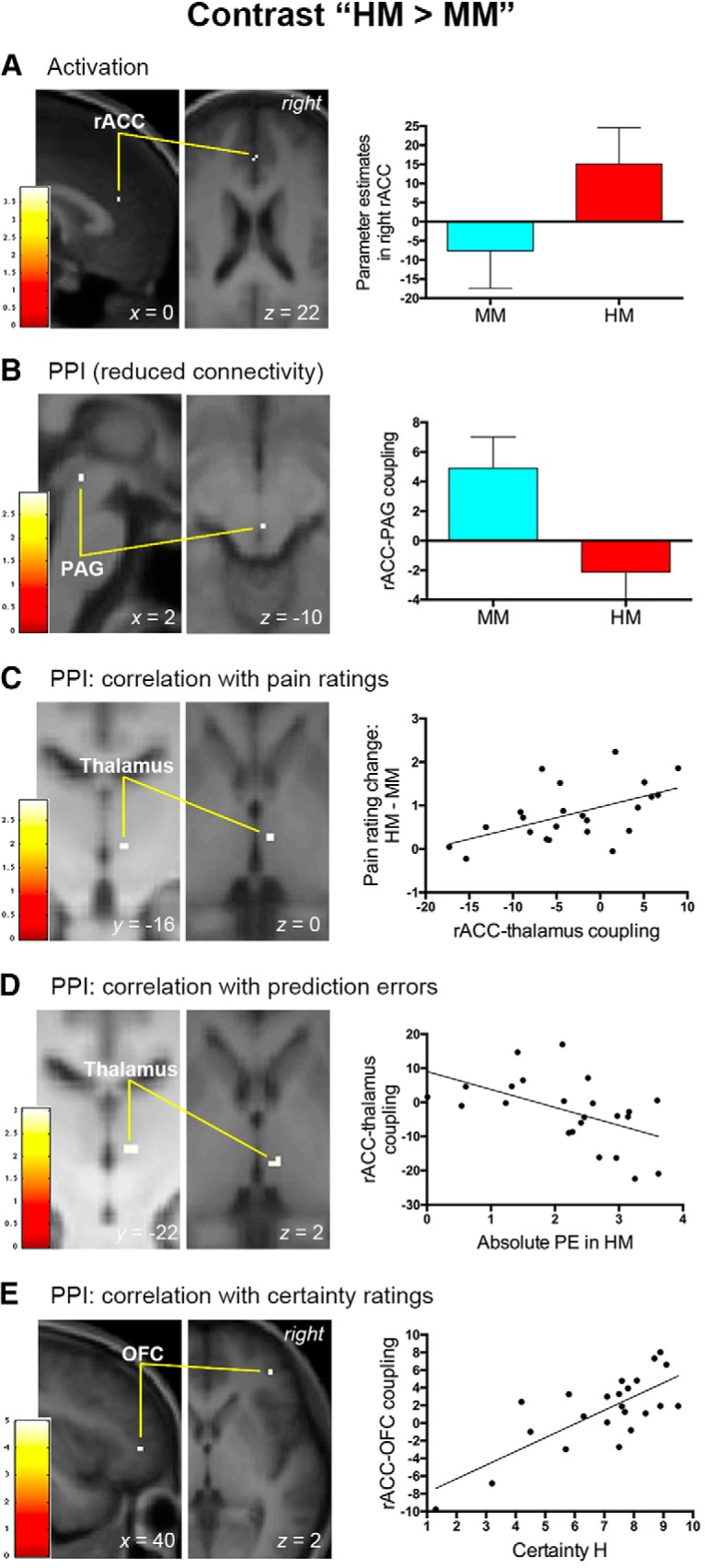
Neural mechanisms associated with negative expectancy effects on pain. This figure shows the results of brain activation and PPI analyses in the right rACC associated with negative expectancy effects on pain. A, Pain modulation by negative expectations entailed increased activation in the right rACC. B, Negative expectations were also accompanied by reduced functional connectivity between the rACC and PAG. C, Functional connectivity between the right rACC and right thalamus predicted the magnitude of pain rating changes provoked by negative expectations. D, The absolute prediction error (PE) of pain engendered in the HM condition was inversely correlated with the rACC–thalamus functional connectivity associated with negative expectations. E, Functional connectivity between the right rACC and right lateral OFC covaried with subjective certainty ratings elicited by a high-pain cue. A–E, Activation clusters survived small-volume corrections (p < 0.05, FWE corrected) and were overlapped on an average structural image. The bar on the left shows the range of t scores for SPM 8. Bar graphs and scatter plots depict parameter estimates extracted from the suprathreshold cluster. Error bars in A and B represent SEM. Scatter plots depict the relationship between behavioral data and the strength of functional connectivity.
