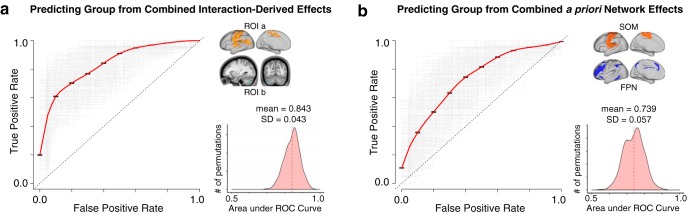
Figure 12.
Diagnostic classification via SVM. SVM classification based on combined thalamic and hippocampal functional connectivity effects. a, Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for a binary classifier predicting group membership (22q11DS or HCs) based on the linear combination of connectivity values (mean Fz) from the thalamus and hippocampus to ROIa and ROIb. Here ROIa and ROIb refer to the interaction-derived effects from the whole-brain analysis shown in Figure 2. The linear combination was obtained in the following way: ([thalamus-to-ROIa + hippocampus-to-ROIb] − [thalamus-to-ROIb + hippocampus-to-ROIa]). This is formally equivalent to an “interactive” effect of thalamic and hippocampal connectivity across the ROIs and produces a single value for classification. Gray represents ROC curves for each of the n = 1000 iterations. Red represents the vertical average. The distribution of areas under the n = 1000 ROC curves (AUC) is plotted on the right, where an AUC of 1 would represent a perfect classifier. b, As presented in a, connectivity to a priori SOM and FPN networks produced a linear combination for the ROC analyses, obtain in the following way: ([thalamus-to-SOM + hippocampus-to-FPN] − [thalamus-to-FPN + hippocampus-to-SOM]). For considerations regarding Type I error protection, see Figure 2 and Figure 9 analyses.