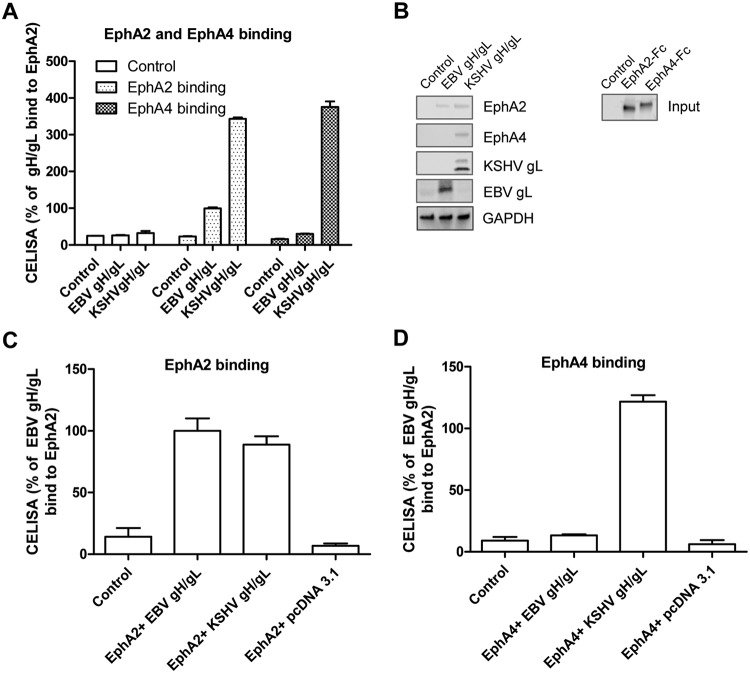
FIG 4.
Both EphA2 and EphA4 bind to KSHV gH/gL. (A) CHO-K1 cells were transiently transfected with control pcDNA3.1, EBV gH/gL, or KSHV gH/gL plasmids. Soluble EphA2-Fc or EphA4-Fc was prepared by transfecting CHO-K1 cells with EphA2-Fc or EphA4-Fc plasmid constructs, and medium supernatants containing EphA2-Fc or EphA4-Fc were overlaid on HEK293T cells expressing EBV gH/gL or KSHV gH/gL in 96-well plates in triplicate for 2 h at 4°C; bound protein was detected using anti-human IgG, which recognizes the Fc portion of the Eph2-Fc and EphA4-Fc by CELISA. (B) CHO-K1 cells seeded in 6-well plates were transfected with control plasmid pcDNA3.1, EBV gH/gL, or KSHV gH/gL with gL containing a Hig tag, as indicated. After 24 h, cells were washed twice with ice-cold PBS and incubated with supernatants from pcDNA3.1 (control plasmid), EphA2-Fc-, or EphA4-Fc-transfected cells isolated 24 h posttransfection for 2 h at 4°C. The cells were then washed with ice-cold PBS three times and lysed with 200 μl of 1 × SDS lysis buffer. Proteins bound to the cells expressing EBV gH/gL or KSHV gH/gL were then analyzed using antibodies to the Fc region of the EphA2 and EphA4 fusions by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Expression of the KSHV gH/L or EBV gH/gL complex was monitored by analyzing KSHV gL or EBV gL expression using anti-His antibodies directed against a His tag added to KSHV gL or polyclonal antibodies directed against EBV gL. (C and D) CHO-K1 cells seeded in 6-well plates were transfected with control plasmid pcDNA3.1, EBV gH/gL, or KSHV gH/gL together with EphA2-Fc or EphA4-Fc. Transfected cells were seeded in 96-well plates in triplicate posttransfection. The cells were then washed with ice-cold PBS three times, and gH/gL-associated EphA2 (C) or EphA4 (D) was determined by CELISA using anti-human IgG antibodies.