Figure 2.
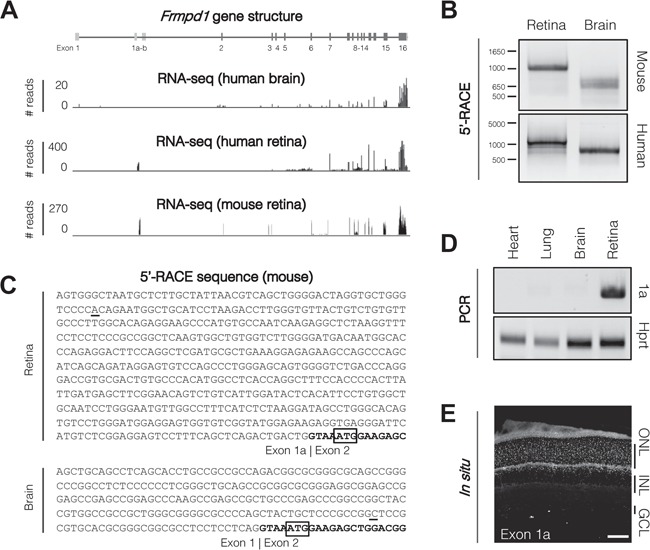
Frmpd1 is transcribed from an alternative promoter in the retina. (A) RNA-seq reveals alternate exon usage in human brain and retina. Frmpd1 exon structure for all three annotated Ensembl splice variants are shown; dark grey boxes indicate protein-coding exons and light grey boxes indicate untranslated exons. Aligned RNA-sequencing reads from adult human brain and retina are represented as a histogram. Human brain reads correspond to Ensembl human transcript ID Frmpd1–202, whereas human retina reads correspond to Frmpd1–203. (B) Tissue-specific RACE products in mouse and human. To determine TSSs used in brain and retina, a primary RACE reaction was performed using a gene-specific primer in Exon 8, followed by a nested RACE reaction using a gene-specific primer in Exon 6 to target both Frmpd1–202 and Frmpd1–203 transcript isoforms. 5′-RACE PCR products were visualized on an agarose gel, purified and cloned into a sequencing vector. (C) Frmpd1 5′-UTR sequences in murine retina and brain. Sanger sequencing of 5′-RACE products revealed the transcription of alternate 5′-UTR sequences in brain and retina. The retina transcript begins with Exon 1a, while brain begins with Exon 1. Both are spliced to Exon 2 (bold) where the translation start site is located (ATG; boxed). (D) Exon 1a expression is limited to the retina. PCR using primers specific for Exon 1a using cDNA from various P21 mouse tissues reveal that it is only expressed in the retina. (E) Localization of Exon 1a RNA in retina. Localization of Exon 1a RNA was assessed by fluorescent in situ hybridization of P21 mouse retina. Scale bar, 50 μm. ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer.
