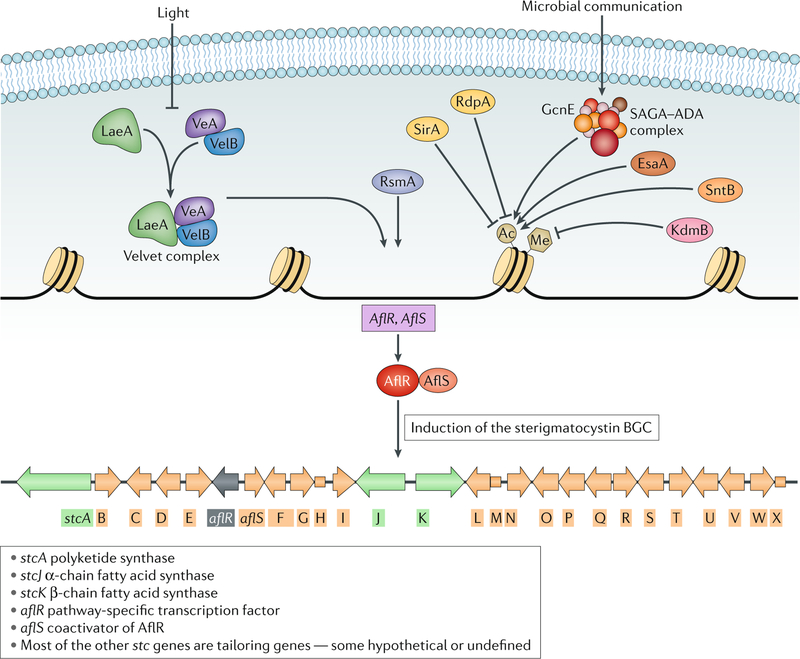
Fig. 2 |. Regulation of the sterigmatocystin biosynthetic gene cluster.
The Aspergillus nidulans sterigmatocystin biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) is one of the most thoroughly studied BGCs at the regulatory level. The pathway-specific regulatory transcription factor, AflR, and its partner, AflS, are induced by specific proteins (for example, RsmA, a basic leucine zipper transcription factor146) and are epigenetically regulated by the Velvet complex66 and chromatin modifiers, including the histone 3 demethylase KdmB63, the histone 4 acetylase EsaA147, the histone deacetylases RdpA65 and SirA148 and the histone reader SntB149. Environmental factors such as light and interactions with other microorganisms or insects also affect the induction of the sterigmatocystin BGC. For example, fungus–bacteria interactions induce the cluster through the histone acetyltransferase GcnE, a member of the histone acetyltransferase SAGA–ADA (Spt–Ada–Gcn5–acetyltransferase–ADA) complex69, whereas white light can repress expression of some BGC-encoded genes39. A schematic of the sterigmatocystin BGC details the structure and encoded genes. Adapted with permission from reF.150, Springer Nature Limited.