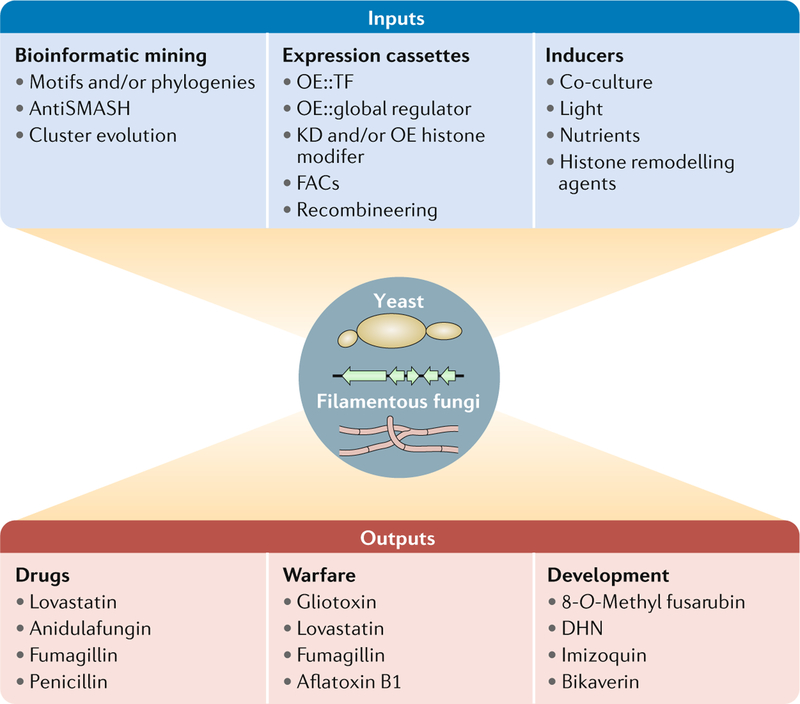
Fig. 4 |. Integration of genome mining with fungal biology yields valuable secondary metabolites.
Biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) can be expressed in either heterologous hosts (typically yeast and Aspergillus spp.) or endogenous filamentous hosts (middle circle). Key input features to select BGCs of interest start with bioinformatic mining of sequenced genomes to eliminate replication and identify uniquegenes. Expression cassettes can be used for gene overexpression, gene deletion, yeast recombineering and fungal artificial chromosome (FAC) construction. Inducers that can activate cryptic BGCs include abiotic stress, epigenetic chemicals, nutrients and co-cultures. Outputs include new drugs that may overlap with endogenous function of the fungus, including warfare and developmental signals. DHN, 1,8-dihydroxynaphthalene; KD, knockdown; OE, overexpression; TF, transcription factor.