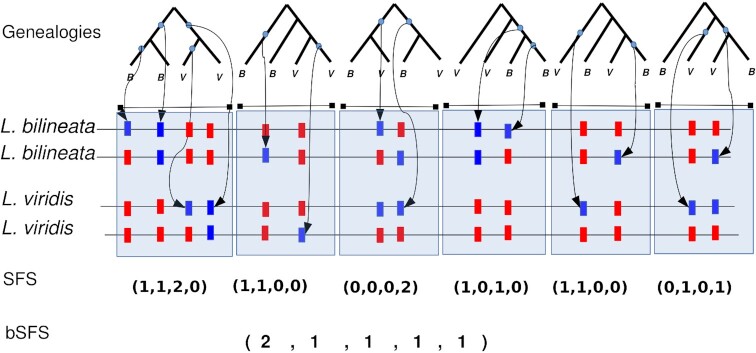
Figure 3:
The folded blockwise site frequency spectrum (bSFS). The variation in alleles represented by different colors (the ancestral state showed in red). Given a single genealogy (a diploid genome from two populations can form six possible genealogies), each block contains four mutation types: (i) unique heterozygous sites in L. bilineata, (ii) unique heterozygous sites in L. viridis, (iii) shared heterozygous sites between L. viridis and L. bilineata, or (iv) homozygous sites that are different between L. viridis and L. bilineata, i.e., homozygous fixed differences. The bSFS (spectrum of SFS) has been calculated by counting the number of occurrences of each SFS.