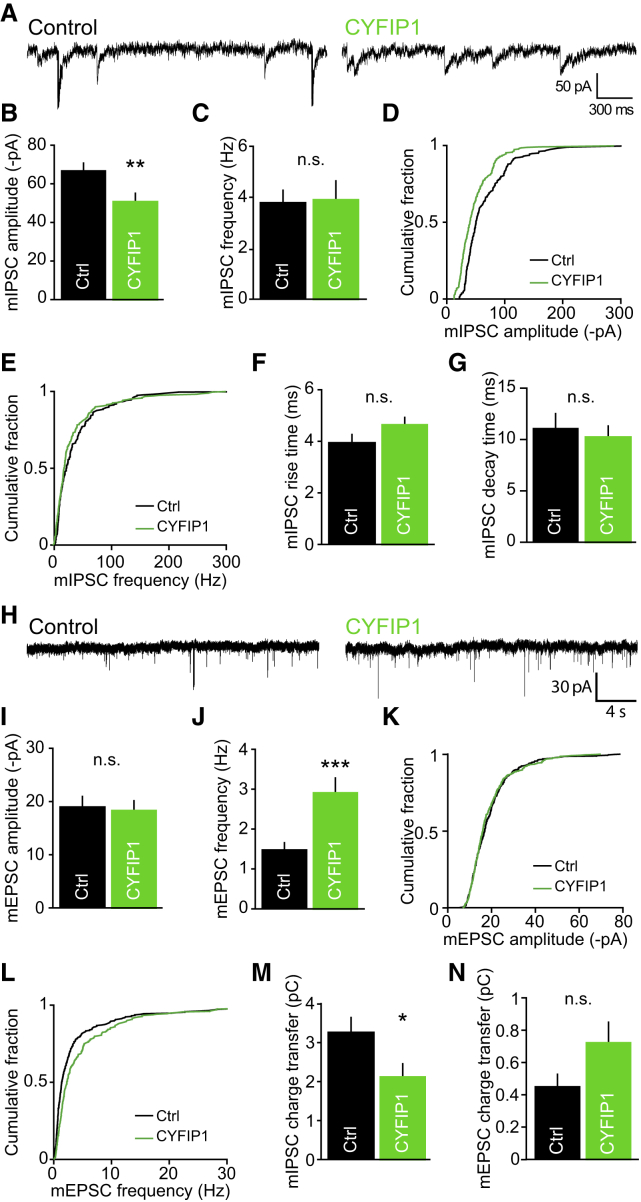
Figure 4.
Increased CYFIP1 Gene Dosage Disrupts Inhibitory and Excitatory Synaptic Transmission
(A) Representative traces of miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) recorded from control GFP (Ctrl) and CYFIP1-overexpressing cultured hippocampal neurons at DIV14–DIV16.
(B and C) Pooled data of mIPSCs showing neurons transfected with CYFIP1 have a reduction in (B) mean mIPSC amplitude but no change in (C) mean mIPSC frequency (mIPSC amplitude: from 66.9 ± 3.8 to 50.7 ± 3.6 -pA, p = 0.0062; frequency: from 3.8 ± 0.5 to 3.9 ± 0.7 Hz; p = 0.92, n.s.; all n = 10 cells from 3 preparations; Student’s t test).
(D and E) Cumulative frequency graphs of mIPSC (D) amplitude and (E) frequency.
(F) Graph of mIPSC rise time kinetics (from 4 ± 0.3 to 4.6 ± 0.3 ms; n = 9 cells from 3 preparations; p = 0.0623, n.s.; Mann-Whitney).
(G) Graph of mIPSC decay time kinetics (from 11.1 ± 1.4 to 10.2 ± 1.1 ms; n = 10–11 cells from 3 preparations; p = 0.618, n.s.; Student’s t test).
(H) Representative traces of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) recorded from CYFIP1 or GFP control (Ctrl) transfected neurons.
(I and J) Pooled data of mEPSCs showing neurons transfected with CYFIP1 have no difference in (I) mean mEPSC amplitude but a significant increase in (J) mean mEPSC frequency compared with control (mEPSC amplitude: from 19.0 ± 1.7 to 17.0 ± 1.4 -pA; p = 0.367, n.s.; frequency: from 1.5 ± 0.1 to 2.9 ± 0.4 Hz, p = 0.0003; n = 14–20 cells from 3 preparations; Student’s t test).
(K and L) Cumulative frequency graphs of mEPSC (K) amplitude and (L) frequency.
(M) Quantification of mIPSC total charge transfer (from 3.3 ± 0.4 to 2.1 ± 0.3 pC; n = 9 cells from 3 preparations; p = 0.0341; Student’s t test).
(N) Quantification of mEPSC total charge transfer (mEPSC charge transfer: from 0.45 ± 0.1 to 0.7 ± 0.1 pC; n = 10–11 cells from 3 preparations; p = 0.1307, n.s.; Mann-Whitney).
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Bars indicate mean, and error bars indicate SEM. See also Figure S2.