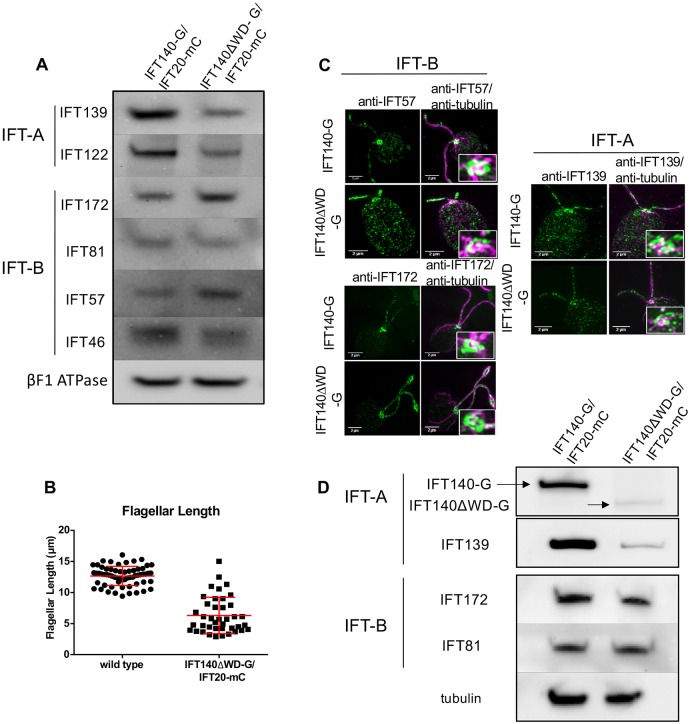
Fig. 4.
Expression of IFT140 lacking its N-terminal WD-repeats results in a partial recovery of IFT-A and formation of half-length flagella with reduced levels of IFT-A. (A) Western blots of WCE from IFT140-G/IFT20-mC and IFT140ΔWD-G/IFT20-mC cells show a partial restoration of IFT-A proteins. Some IFT-B protein levels were slightly increased. βF1 ATPase is the loading control. (B) Flagellar-length measurements for wild-type and IFT140ΔWD-G/IFT20-mC cells. Wild-type flagella are ∼12.5 µm long (n=63 flagella) whereas IFT140ΔWD-G/IFT20-mC flagella averaged about 6.5-µm long (n=43 flagella). Approximately 50% of IFT140ΔWD-G/IFT20-mC cells were flagellated under normal culture conditions; cells without flagella were not included in the analysis. (C) SIM images of IFT140-G and IFT140ΔWD-G cells labelled with anti-tubulin and anti-IFT57, anti-IFT172 or anti-IFT139 antibodies. Expression of IFT140ΔWD-G led to partial recovery of IFT-A in the basal body region and in the flagella. Scale bars: 2 µm. (D) Western blots of isolated flagella of IFT140ΔWD-G/IFT20-mC and control cells. IFT140-G and IFT140ΔWD-G were detected with anti-GFP; IFT139, IFT172 and IFT81 were detected with antibodies against those proteins; and tubulin, which was the loading control, was detected with anti-acetylated tubulin.