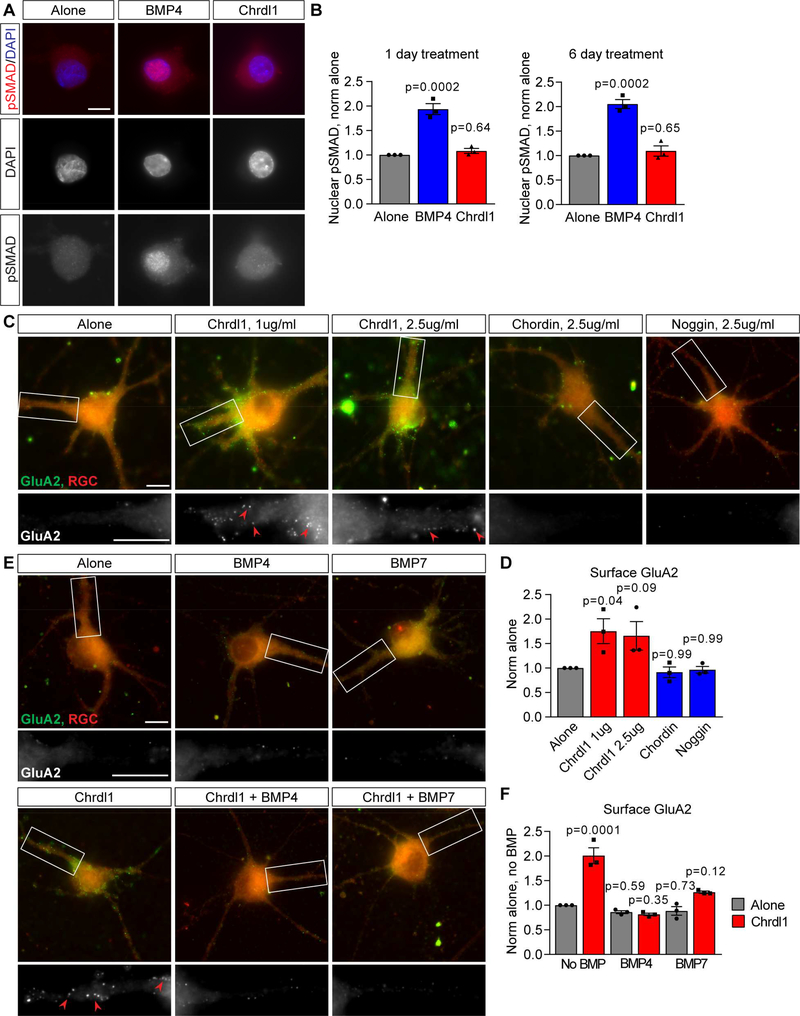
Figure 3. Chrdl1-induced GluA2 clustering is independent of BMP signaling.
(A,B) Chrdl1 does not regulate recruitment of pSMAD to the nucleus in RGC neurons. (A) Example images of RGCs treated with 1μg/ml Chrdl1 or 250ng/ml BMP4 for 1 day, and immunostained for pSMAD (red) and DAPI to mark the nucleus (blue). BMP4 is a positive control condition, and is sufficient to increase nuclear pSMAD. (B) Quantification of A, nuclear pSMAD level normalized to alone. N=3 experiments, each experiment 30 cells/condition, both 1 day and 6 day treatment. (C,D) Other secreted BMP antagonists do not increase surface clustering of GluA2 in RGCs. (C) Example images of RGC neurons treated with Chrdl1, chordin or noggin for 6 days, concentration as marked. Top panel, red labels neuron, green surface GluA2. Bottom panel, zoom of dendrite, GluA2 white. Arrowheads mark example GluA2 clusters. (D) Quantification of C, surface GluA2 compared to RGC neurons alone (untreated). N=3 experiments, each experiment 30 cells/condition. (E,F) Excess BMP ligands block the ability of Chrdl1 to increase surface GluA2 clustering in RGCs. (E) Example images of RGC neurons treated with 1μg/ml Chrdl1, 250ng/ml BMP4, 250ng/ml BMP7, or Chrdl1 and either BMP for 6 days. Top panel, red labels neuron, green surface GluA2. Bottom panel, zoom of dendrite, GluA2 white. Arrowheads mark example GluA2 clusters. (F) Quantification of E, surface GluA2 normalized to RGCs alone (no BMP). N=3 experiments, each experiment 30 cells/condition. Scale bar = 10μm. Bar graphs mean±s.e.m., with individual data points representing experiments. Statistics by one-way ANOVA, significance as stated on graph compared to alone. See also Figure S1, Table S2, S3.