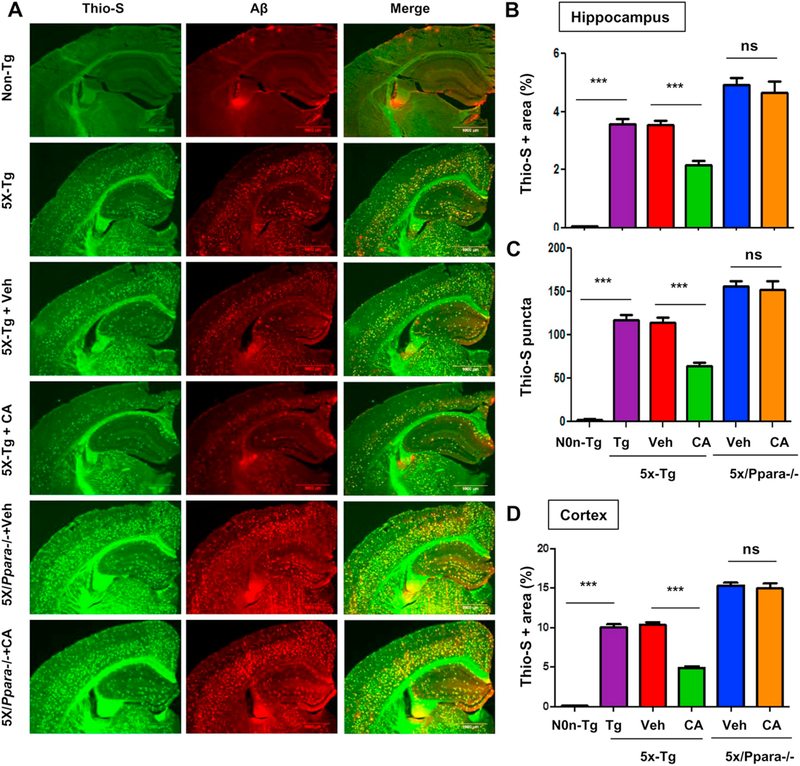
Fig. 7.
Cinnamic acid lowers plaque deposition in a PPARα-dependent manner. Six months old 5×FAD mice (n = 8/group) and 5XFAD mice null for Ppara (5X/Ppara−/−) (n = 5/group) were treated orally with cinnamic acid (100 mg/kg/day) or vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose) daily for one month after which (A) the cerebral amyloid plaque burden was monitored by colabeling hippocampal sections with thioflavin-S and Aβ monoclonal antibody 6E10. (B-D) Quantitative analysis of (B) hippocampal thio-S area fraction, (C) hippocampal thio-S positive puncta count and (D) thio-S positive area fraction in the cortex. Quantification was performed using the ‘analyze particle’ feature in ImageJ. All data represents mean ± SEM. One way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test was used for statistical analysis; * p < .05; ** p < .01; *** p < .001.