Figure 5.
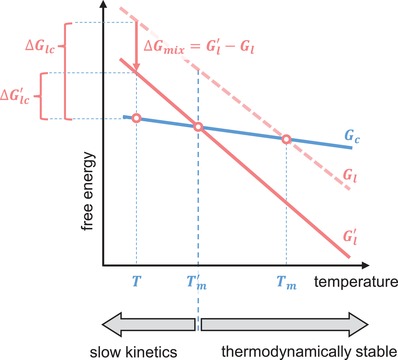
Illustration of the impact of mixing on the melting temperature, which decreases from Tm to , and driving force for crystallization at temperature T, which decreases from ΔG lc to , where Gc, Gl, and are the Gibbs free energy of the crystalline state (Gc of only one component is shown for clarity), of the single‐component liquid, and of the multicomponent liquid, respectively. Above , the multicomponent liquid is thermodynamically stable, whereas below the crystallization kinetics are slowed due to a reduced .
