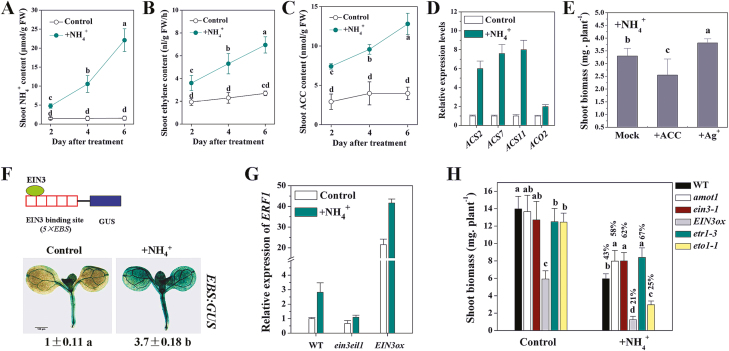
Fig. 4.
Effects of ethylene on shoot growth tolerance to NH4+. (A) NH4+ content in Arabidopsis shoots for the duration of the NH4+ treatment. (B) Ethylene evolution in Arabidopsis shoots for the duration of the NH4+ treatment. (C) 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) content in Arabidopsis shoots for the duration of the NH4+ treatment. Seedlings at 5 d after germination were exposed to NH4+ for varying treatment times, and NH4+ content (A), ethylene evolution (B), and ACC content were determined. Values are means ±SD of three replicates. Different letters indicate statistical differences at P<0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Duncan post-hoc test). (D) Effect of NH4+ treatment on shoot ACS and ACO genes expression by qRT-PCR for 6 h. Values are means ±SD of three replicates. CBP20 was used as the internal reference gene, and the control was considered as 1. (E) Effect of supplied ethylene inhibitors 30 μM AgNO3 and 25 μM ACC on shoot biomass of WT seedlings grown in 40 mM NH4+ treatment medium. Values are the means ±SD, n=10–12. (F) Schematic diagram of the EIN3 activity reporter system showing the EIN3 protein, five tandem repeats of the EBS (5×EBS), and the GUS gene. Expression of 5×EBS:GUS in leaves of the WT under control conditions and 24 h NH4+ treatment. One representative sample from each treatment (10 plants) is shown. GUS staining intensity was quantified using Image J software, and the control was considered as 1. Values are means ±SD of three replicates. (G) Effect of NH4+ treatment on shoot ERF1 gene expression of WT, ein3eil1, and EIN3ox lines by qRT-PCR for 6 h. Values are means ±SD of three replicates. ACTIN2 was used as the internal reference gene, and the WT control was considered as 1. (H) Effect of NH4+ treatment for 6 d on shoot fresh weight of WT, amot1, ein3-1, EIN3ox, etr1-3, and eto1-1 seedlings. Values are the means ±SD, n=12. Different letters indicate statistical differences at P<0.05 of control and NH4+ treatment, respectively (one-way ANOVA with Duncan post-hoc test).