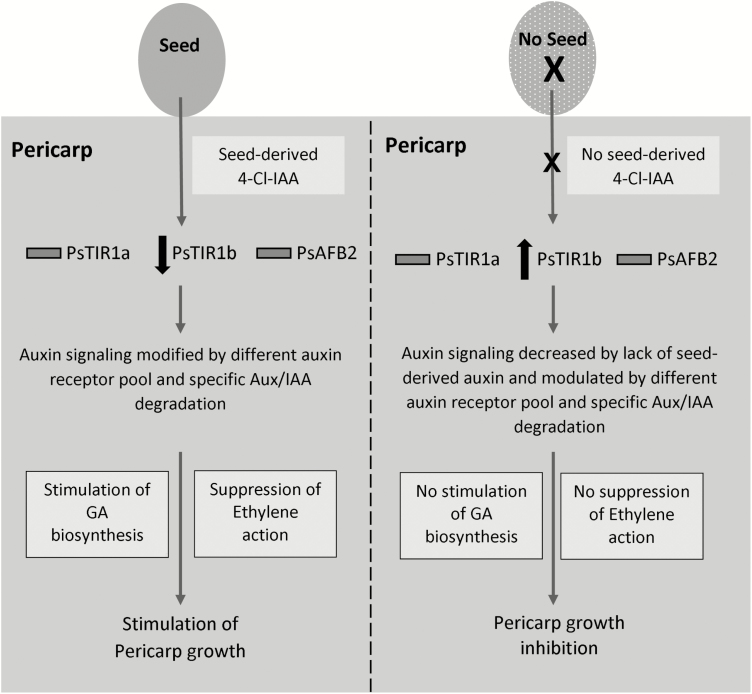
Fig. 8.
A working model for seed and auxin (4-Cl-IAA) stimulation of pea fruit growth. 4-Cl-IAA in the seed is transported to the pericarp, which leads to modulation of the pericarp auxin-receptor pool (through a decrease in PsTIR1b transcript abundance) that targets the degradation of specific Aux/IAA proteins, resulting in auxin-related changes in gene expression that facilitate pericarp growth. These seed/4-Cl-IAA-induced changes include the stimulation of GA biosynthesis and the suppression of ethylene action in the pericarp. In the absence of developing seeds, the lack of seed-derived auxin (4-Cl-IAA) modifies the make-up of the pericarp auxin-receptor pool (as noted by an increase in PsTIR1b transcript abundance) and reduces auxin signaling and activity, thus inhibiting pericarp growth.