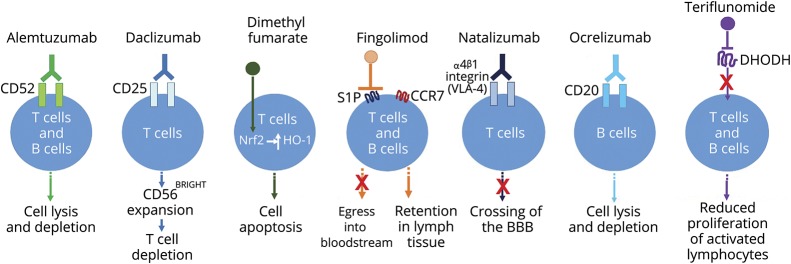
Figure. Simple schematic depicting the general effects of selected DMTs on lymphocytes.
The mechanisms of action of each DMT have not been fully elucidated in relapsing MS; the depiction shown in this schematic with respect to effects on lymphocytes is based on currently available evidence. Alemtuzumab is a humanized immunoglobulin-1 monoclonal anti-CD52 antibody that results in rapid lysis of lymphocytes.42 Daclizumab is a humanized monoclonal anti-CD25 antibody that leads to CD56BRIGHT expansion via interleukin-2 modulation, and consequently, to activated T-cell depletion.14 Dimethyl fumarate is believed to exert its lymphopenic effect through activation of the Nrf2 pathway, which leads to induction of the anti-inflammatory stress protein HO-1 and consequently apoptosis of primarily CD8+ T cells.8,34 Fingolimod is a sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) agonist; after binding to and activating S1P1, fingolimod acts as a functional antagonist and prevents CCR7+ lymphocytes, including naïve and central memory T cells and B cells, from exiting lymph nodes.7,8 Natalizumab is a humanized monoclonal anti-α4 integrin antibody that binds α4β1 integrin (very late antigen-4 [VLA-4]) and prevents lymphocytes from crossing the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and entering the CNS.14 Ocrelizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody directed against CD20-expressing B-cells; it results in antibody-dependent cellular cytolysis following cell surface binding to B lymphocytes.49 Teriflunomide inhibits de novo pyrimidine synthesis in rapidly dividing cells by inhibiting the enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), causing a cytostatic effect on activated/proliferating T and B cells.14