Fig. 1. Illustration of the signaling system.
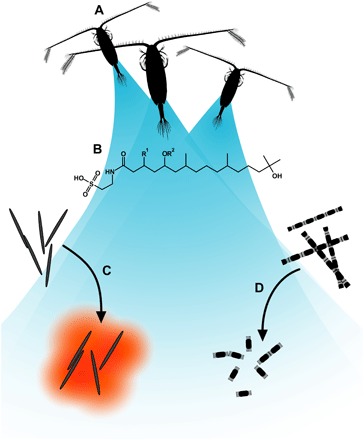
(A) The copepod Calanus sp. emits copepodamides. (B) General structure of copepodamides. Copepodamides are known to induce toxin formation in dinoflagellates. (C) We explore whether copepodamides induce toxin formation in other algae, such as P. seriata, infamous for its production of the neurotoxic alkaloid domoic acid. (D) We also test whether copepodamides are responsible for grazer-induced colony size plasticity seen in other dominating phytoplankton such as S. marinoi.
