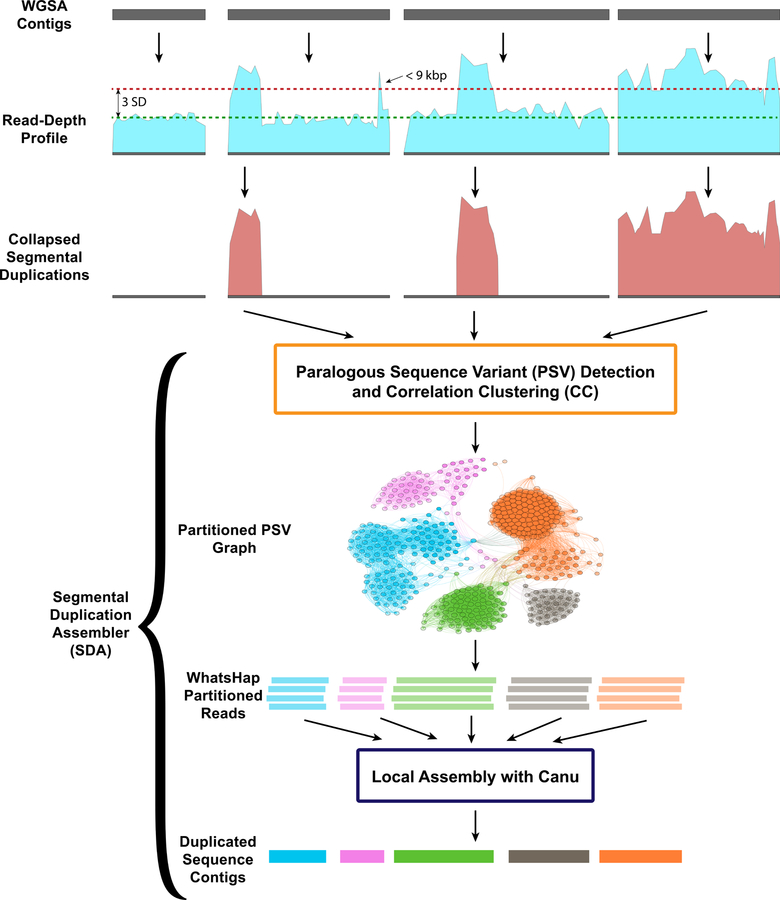
Figure 1. Flowchart of Segmental Duplication Assembler (SDA) method.
Regions of collapsed SDs are defined by assessing whole-genome shotgun (WGS) sequence read-depth profiles using BLASR across sequence contigs generated from a de novo WGSA. Regions (>9 kbp in length) with elevated sequence coverage (three standard deviations plus the mean) and not entirely composed of common repeats are considered collapsed SDs. Sequence reads corresponding to the collapsed SDs are recovered and examined for variants at each position along the collapse. Single-base-pair substitutions that appear at the same threshold as unique sequencing depth are identified and flagged as paralog-specific variants (PSVs) effectively partitioning reads into PSV clusters (WhatsHap). Sequence reads assigned to each PSV cluster are independently assembled using Canu and error-corrected using Quiver.