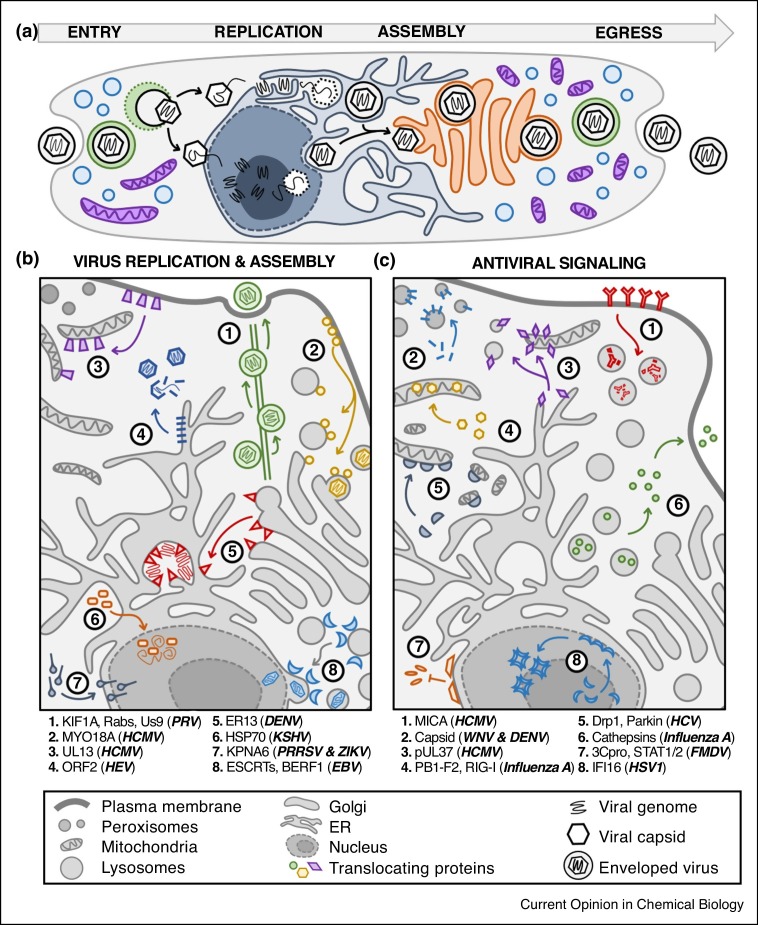
Figure 2.
Virus infection causes the translocations of both host and virus proteins. (a) Viruses have diverse spatial-temporal strategies to enter the cell, replicate their genomes, assemble virions, and egress to infect a new host. (b) Translocations of host and virus proteins are critical for using cellular machineries for virus replication, assembly, and egress. (c) Host antiviral signaling relies on protein translocations between organelles, and viruses can disrupt these movements or translocate viral proteins to attenuate immune response. Abbreviations: endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRTs), MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence A (MICA), signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT).