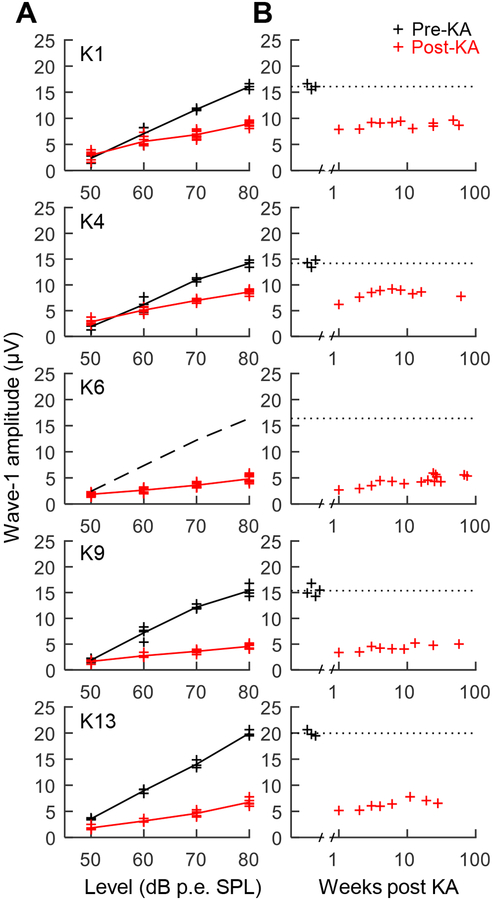
Fig. 2.
Auditory brainstem response (ABR) wave 1 amplitude as a function of click presentation level (A). Data are from before (black) and ≥4 weeks following (red) bilateral exposure to kainic acid (KA). KA reduces wave 1 amplitude at moderate to high sound levels by 40–70% across animals. The dashed black line drawn for K6 indicates mean wave-1 amplitude prior to KA in the other animals because pre-exposure control data were unavailable. Change over time in ABR wave 1 amplitude following KA exposure (B). Click level was 80 dB peak equivalent (p.e.) SPL. KA exposure causes long term reduction of wave 1, consistent with permanent auditory nerve (AN) injury.