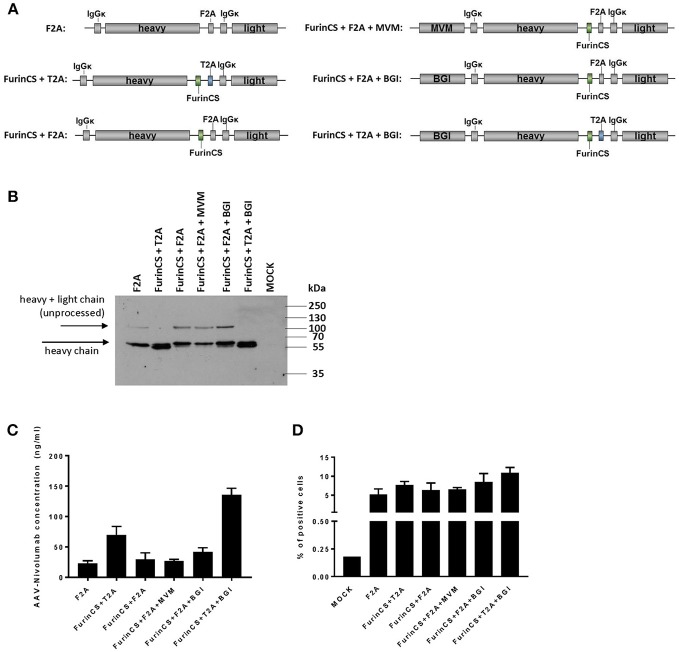
Figure 8.
Optimization of nivolumab expression and processing. (A) Schematic drawings of optimized nivolumab expression constructs for AAV2 transfer vectors. All vector constructs were under control of the SFFV promoter. F2A, foot and mouth disease virus-derived self-cleaving protein sequence; T2A, thosea asigna virus-derived self-cleaving protein sequence; FurinCS, furin cleavage site; MVM, minute virus of mice intron; BGI, β-globin intron; IgGκ signal peptides are fused to the N-terminal ends of heavy and light chain. (B) Four days after transduction of MDA-MB-453 cells with small-scale preparations of AAV2 vector encoding the different constructs (500,000 genome copies/cell), cell culture supernatants were collected and analyzed by Western blot analysis using an IgG-Fc-specific antibody. AAV2GFP-transduced cells served as control (MOCK). (C) AAV-encoded nivolumab released into the vector transduced MDA-MB-453 cell culture supernatant was assessed by sandwich ELISA using plates coated with recombinant PD-1 and an IgG-Fc-specific detection antibody. (D) Specific antigen recognition was evaluated on PD-1 positive cells (MOLT4.8) by flow cytometry. The binding of nivolumab was detected via an IgG-Fc-specific antibody. MOLT4.8 cells were treated with supernatant of AAV2IgG−Fc transduced cells (MOCK). All datasets in (C,D) n = 3 (mean ± SD).