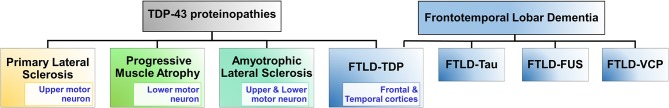
Figure 1.
TDP-43 proteinopathies. TDP-43 proteinopathies refer to the diseases where TDP-43 is implicated and it includes: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD-TDP), primary lateral sclerosis, and progressive muscular atrophy. FTLD is a group of disorders principally of the frontal temporal lobes of the brain causing dementia. Other forms of FTLD disorders are FTLD-Tau, FTLD-FUS, and FTLD-VCP. FTLD-Tau is associated with mutations in the MAPT gene which encodes microtubule associated protein, Tau. Tau's misfolding and aggregation lead to loss of microtubule-binding function and formation of neuronal and glial inclusions (Irwin et al., 2015). FTLD-FUS is associated with mutations in the RNA-binding protein FUS, which results in disruption of its nuclear localization and leads to its accumulation into inclusion bodies (Mackenzie et al., 2011). FTLD-VCP is associated with mutations in the valosin-containing protein (VCP). FTLD-VCP manifests ubiquitin and TDP-43-positive neuronal intranuclear and cytoplasmic inclusions. FUS, fused in sarcoma; TDP-43, TAR DNA binding protein 43; VCP, valosin containing protein.