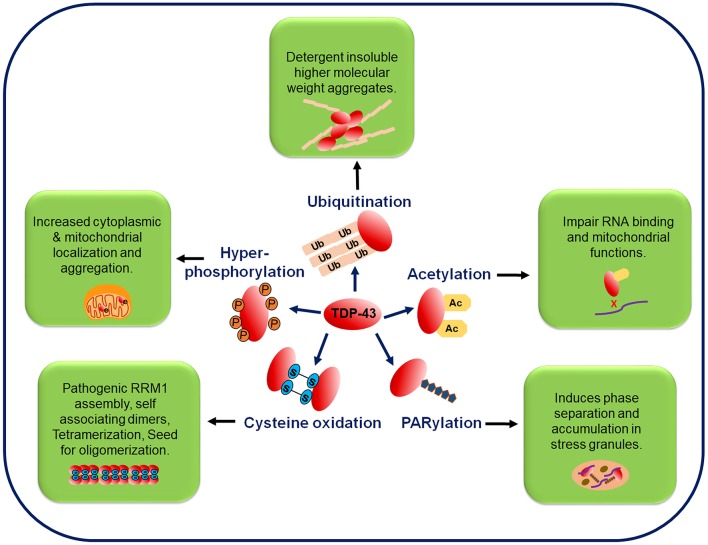
Figure 4.
Post-translational modifications in the TDP-43 protein. TDP-43 undergoes several post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, ubiquitination, acetylation, PARylation, and cysteine oxidation. Phosphorylation of the full-length and C-terminal fragments of TDP-43 is a pathological hallmark of ALS and is associated with its increased cytoplasmic mislocalization. In FTLD and ALS brain inclusions, pathological TDP-43 is found in the ubiquitinated state and mutations at the ubiquitination sites decrease the TDP-43 aggregation. Acetylation promotes accumulation of the insoluble and hyper-phosphorylated TDP-43 aggregates. PARylation promotes the phase separation of TDP-43 into stress granules. Oxidative stress mediated cysteine oxidation promotes the oligomerization and aggregation. Ac, acetylation; P, phosphorylation; PARylation, poly ADP ribosylation; Ub, ubiquitination.