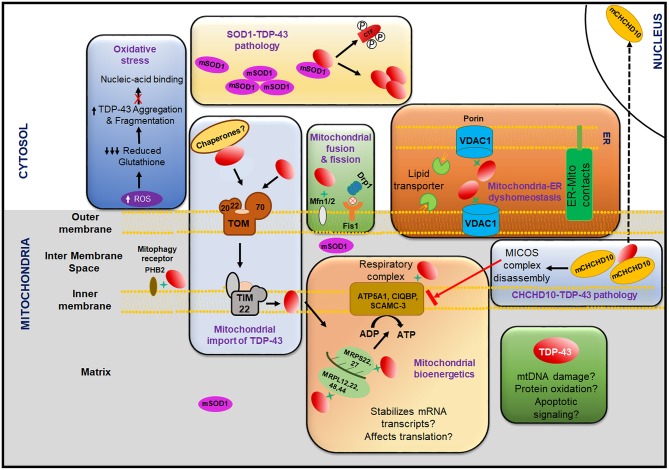
Figure 7.
Role of mitochondria in the TDP-43 pathology. TDP-43 mediated dysfunction of the mitochondria leads to increase in the production of ROS that causes decline in the reduced glutathione levels which in turn can increase the aggregation of TDP-43 and also inhibit TDP-43 from binding to the nucleic acid. Mutant SOD1 can cause cytoplasmic mislocalization, fragmentation, phosphorylation and aggregation of TDP-43. Inhibition of the interaction of the mitochondrial fission proteins Drp1 and Fis1 greatly reduces the mitochondrial dysfunction caused by the TDP-43 overexpression/aggregation. TDP-43 also disrupts the ER-mitochondrial contacts which can have potential implications to the calcium signaling, ATP production and lipid transport. TDP-43 is imported into mitochondria via the outer membrane complex (TOM70) and across the inner membrane via TIM22. Several factors like chaperones and mitochondrial membrane potential might play a role in the TDP-43 import. After internalization, TDP-43 is found to interact with several proteins involved in the mitochondrial translation machinery (MRPS22, 27 and MRPL12, 22, 48, 44) and the mitochondrial respiratory complex (ATPA, CIQBP, SCAMC-3). TDP-43 also perturbs the translation of ND3/6 of the respiratory complex I and thus severely impairs the mitochondrial bioenergetics and reduces the ATP production. TDP-43 overexpression alters the CHCHD10 localization from the mitochondria to the nucleus and the loss-of-function mutations in CHCHD10 are associated with MICOS complex disassembly and may negatively regulate the assembly of the respiratory complex. TDP-43 also interacts with other crucial mitochondrial proteins including the mitochondrial fusion protein Mfn2 and the mitophagy receptor PHB2. TDP-43 is depicted here by the red oval structure. TDP-43 interaction with the mitochondrial proteins are depicted via green star. Inhibition is denoted by red cross mark. ATPA, ATP synthase subunit A; CHCHD10, coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain containing 10; CIQBP, complement component 1Q binding protein; CTF, C-terminal fragments; Drp1, dynamin related protein 1; ER-Mito contacts, endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-mitochondria contacts; Fis1, fission 1 (mitochondrial); Mfn2, mitofusin-2; MICOS, mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system; MRPL, mitochondrial ribosomal protein (large subunit); MRPS, mitochondrial ribosomal protein (small subunit); ND, NADH dehydrogenase; P, phosphorylation; PHB2, prohibitin-2; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SCAMC-3, small calcium-binding mitochondrial carrier protein 3; SOD1, superoxide dismutase 1; TIM, translocase of inner membrane; TOM, translocase of outer membrane.