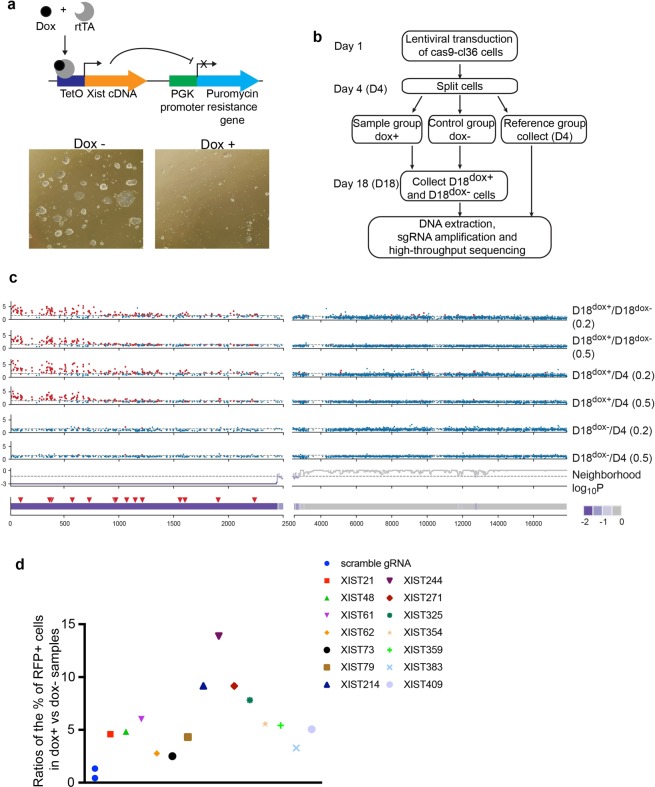
Figure 1.
Tiling CRISPR identifies a 5′ region corresponding to a sgRNA cluster, as a potential Xist silencing domain. (a) Upper Panel: Schematic showing reporter system in which Xist induction is inversely correlated with expression of a puromycin resistance gene. Lower Panel: Representative images of Cl36 cells 4 days after culturing in puromycin-containing medium with or without 1 μg/ml doxycycline. Results indicate robust cell death following Xist induction. (b) Screening work flow. (c) Detection of enriched sgRNAs and enriched sgRNA clusters. The top 6 panels show enrichment profiles of individual sgRNAs among indicated samples. Dashed horizontal lines represent a FC level of 1.5. In panels 1–4, 197 sgRNAs that are significantly enriched with maxFC ≥ 1.5 and RSA p < 0.5 in D18dox+ samples are colored in red and the rest in blue. Among them, 3 sgRNAs are also enriched in D18dox− samples (highlighted in red in panels 5–6). The 7th panel shows neighborhood Log10P for each sgRNA within a sliding window. These values were used to identify an sgRNA-enriched cluster (see Methods). The bottom schematic shows a ~2.4 kb Xist region corresponding to an enriched sgRNA cluster, as determined by neighborhood Log10P. Red triangles represent 14 individual sgRNAs used for validation and downstream analysis. (d) Upon being transduced with an indicated sgRNA, cas9-cl36 cells were split into two groups with one group treated with doxycycline (dox+) and the other with DMSO (dox−). After 7 days continued culturing in puromycin, the ratio of the percentage of RFP+ cells in dox+ vs dox− samples were calculated.