Figure 4.
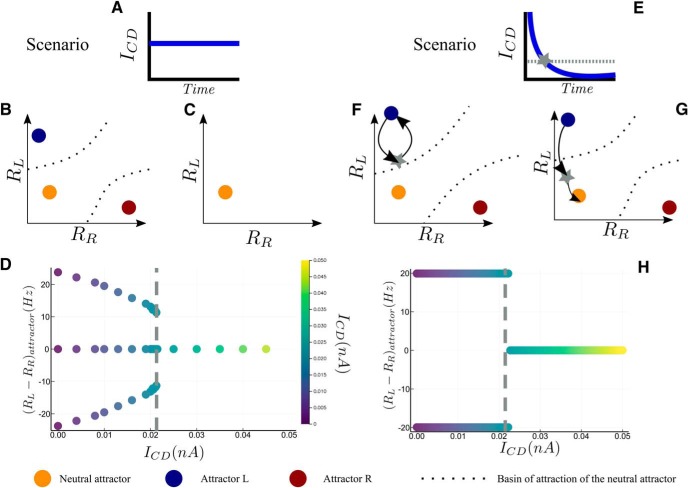
Bifurcation diagram of sequential decision-making, for two scenario of ICD. A, Scenario with a constant value of the inhibitory current for B–D. B, Phase plane representation of the attractors at low ICD (below the critical value). C, Phase plane representation of the attractor landscape at high ICD (above the critical value). Only the neutral attractor exists, corresponding to D (right). D, Attractors state (as the difference in firing rates, RL − RR) with respect to ICD. The gray line, at ICD = 0.0215 nA, represents the bifurcation point. On the left side three attractors exists, on the right side only the neutral one exists. The case without inhibitory current corresponds to ICD = 0 nA. E, Scenario with an inhibitory current decreasing exponentially with time, for F–H. The dashed line corresponds to ICD = 0.0215 nA, value at which the bifurcation at constant ICD occurs (D). The time at which the current amplitude crosses this value is denoted by the gray star in E and F. F, Schematic phase-plan dynamics corresponding to the left side of H. The blue attractor corresponds to the starting point and the black arrow represents the dynamics. At the time ICD becomes lower than 0.0215 nA (gray star), the system is still within the basin of attraction of the initial attractor. Hence, it goes back to the initial attractor. G, Schematic phase-plan dynamics corresponding to the H (right). At the time ICD becomes lower than 0.0215 nA, the system lies within the basin of attraction of the neutral attractor. Hence, the dynamics continues toward the neutral attractor. Those conditions are the ones needed for sequential decision-making. H, Attractors that can be reached when starting from a decision state, for the relaxation dynamics under the scenario represented on E. On the left side of the dashed gray line, the value of ICD,max is too weak and the network remains locked to the attractor corresponding to the previous decision state. On the right side the network dynamics lies within the basin of attraction of the neutral attractor, allowing the network to engage in a new decision task.